Dynamic Programming is a general algorithm design technique for solving problems defined by or formulated as recurrences with overlapping sub instances. Invented by American mathematician Richard Bellman in the 1950s to solve optimization problems. “Programming” here means “planning”
Main idea: 1. set up a recurrence relating a solution to a larger instance to solutions of some smaller instances 2. solve smaller instances once -record solutions in a table -extract solution to the initial instance from that table KEY IDEA -storing solutions to sub-problems rather than re-computing them a. Before any recursive call, say on sub problem Q, check the dictionary to see if a solution for Q has been stored. -If no solution has been stored, go ahead with recursive call. -If a solution has been stored for Q, retrieve the stored solution, and do not make the recursive call. b. Just before returning the solution, store it in the dictionary Memoization for Dynamic Programming a. avoid calculating the same thing twice, b. usually by keeping a table of known results that fills up as sub-instances are solved. Some Problem that can be solved using Dynamic Programming
•Computing a binomial coefficient •Longest common subsequence • Warshall’s algorithm for transitive closure • Floyd’s algorithm for all-pairs shortest paths • Matrix Chain Multiplication. • Constructing an optimal binary search tree • traveling salesman • knapsack problem
Using Dynamic Programming Approach to solve few Problems
1. Fibonacci numbers by DP
memo = { }
fib(n)
if n in memo : return memo[n]
if n=1 : f=0 or n=2: f=1
else f=fib (n-1)+fib(n-2)
memo[n]=f
return f
2. Knapsack Problem by DP
Problem Statement - Given n items of integer weights: w1 w2 … wn
values: v1 v2 … vn
and a knapsack of integer capacity M
We need to find most valuable subset of the items that fit into the knapsack.

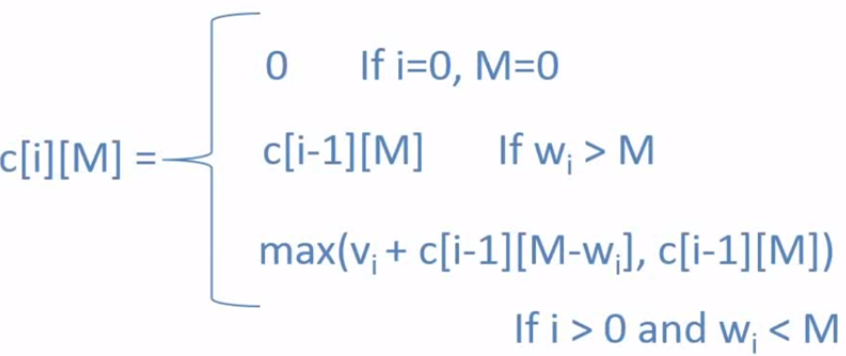
3. Matrix Multiplication by DP Goal - to find the optimal sequence to perform minimum multiplications

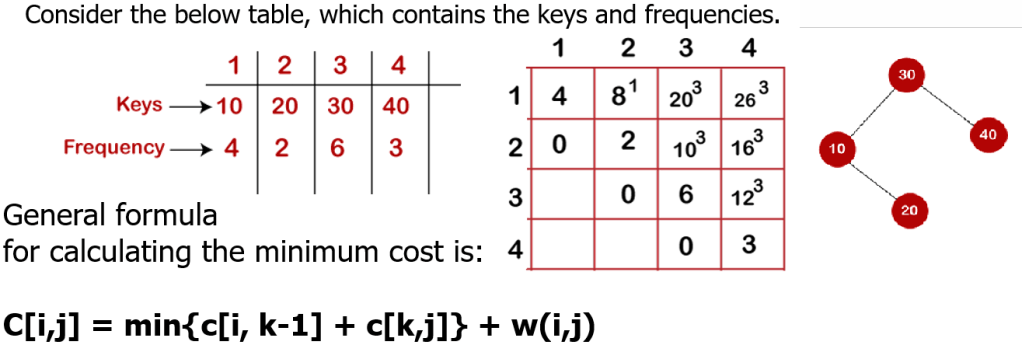
3. Optimal Binary Search Trees by DP It is structure that ensures the minimum number of searches when the frequency of each search is given. Given a sorted array keys[0.. n-1] of search keys and an array freq[0.. n-1] of frequency counts, where freq[i] is the number of searches to keys[i]. Construct a binary search tree of all keys such that the total cost of all the searches is as small as possible.
Lets explore the following videos to develop good understanding of DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING. [Click the following links to watch the video]
- Introduction to Dynamic Programming
- Solving Knapsack Problem by dynamic programming
- Matrix Multiplication using dynamic programming
You are invited to raise queries by writing your question in the box given below
