ADT is basically a mathematical model of data-type, when we talk about data type; it is something that refers two things, a set of values and set of operations.
Set of values means it defines a range of values, you might have been using different data types in the different programming language like (int, char) whichis very fundamental data type in C language. When we say int in C language, it defines a range of values it allows you to use; it goes from -32768 to +32768. It consumes two bytes of memory space.
Set of operations are allowed on this data type, for ex, with type int you’re allowed to do addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. It means that these are the different operations which are allowed with this data type.
When we talk about ADT, it basically describes two things i.e. data-structures and of set of operations, which means that defined set of operations can be performed on these data-structures.
Definition of ADT – it is described as a set of objects sharing the same properties and behaviour. You can relate this definition with the definition of class which defines ‘Class’ as collection of similar object. Class is basically a representation of an ADT. You have been using ‘classes’ in a program which are actually a sort of ADT. Note that class defines two things
- Attributes – every class must have some attributes which define the characteristics of the class
- Behavior – these are the operations or the functions which you defined inside the class
When we talk about ADT, itmust have some properties for the data which is actually the attributes and it also has the behavior or the operations or the functions.
Next, big question would be that how we are going to implement this concept in programming language? We have two terms that we have been using in programming language, one is called encapsulation and the other is called abstraction. These two concepts help us to understand the implementation of an ADT in our programs.
Encapsulation is basically a binding of these data elements and the member functions together into one structure. So we have data elements, member functions and we are binding it together into in a one block and we are calling it as class. class basically provides an encapsulation and the main objective of encapsulation is data hiding, means we don’t want that our data to be accessed directly by the outside world. We also do the data hiding analysis with the help of the access modifiers.
We have access modifiers in the programming language like a private, public, protected. Data hiding that we achieve with the private access modifier, will actually hide the data to be accessed from the users or from the outside world.
The second concept is abstraction; it basically provides the hiding the complexity. It basically provides a higher level view to the user, it means with the help of abstractions we can hide the lower level implementation i.e. we will hide the complexity, it only allow the users to just look to the objective of this function and accordingly can use it.
Generally, when we use any functions using a library, we only concern with the name of the function, the input it requires and the output that it gives/returns. We are not allowed to see the entire definition (i.e. the logic used inside). Abstraction is to hide the technical details of any entity in use.
Abstractions is visible at many places in our day to day activities, whatever the objects we are using, whatever the things we are using is actually provided to us in the abstract form, for ex. if you want to use air condition (AC) in your room then you only need to know that how to start (switch-on) this AC, you need a remote and will require only to press the ‘on’ button and it will start working. It is not required for you to understand the entire technicality that how the things are working behind the scene and how you are getting this cool air. Similarly many things that we are using, is provided to us in abstract form where we only concerned with a higher level view.
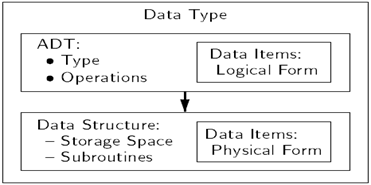
Data items that we are using have two different views or format, one is called logical form and the other is known as physical form. The other names which are quite popular are called internal and external.
logical form refers to external view or you can say it basically provides the conceptual view to the user, it will provide the conceptual details about the attributes provided within the ADT, the operations provided within the ADT.
physical form refers to the internal view or you can say it deals with the implementation part. Basically it refers that how actual data to be stored inside the memory, what are the different organization we are using to arrange our data and how the data to be accessed by the user.
Data structure deals with the implementation part of ADT, when we say ADT, it means abstract data type so here the term abstract refers that it provides only implementation independent view, it means that a user does not allow accessing the implementation detail.
When we talk about the data type we have a logical view (ADT) of the data and then we have a physical view of the data (data-structures)
Understanding the concept of ADT is important because with the proper understanding you carefully identify which data is actually suitable for your program which will improve the performance of your program, the efficiency of the overall program will be enhanced.
Assume that there is one problem to be solved, let’s say problem p. In order to solve the problem you are writing some algorithm. When you write program using the identified algorithm, you are using different data structures you might be using priority-queue or a union-find or simply array. For the same algorithm if we use different data structures you will realize that the performance may be varying so it is very important for a programmer to identify the proper data structures to enhance or to improve the performance of the program.
ADT is also defined using two terms that is specification and design.
Specification describes how the operations behave. Basically it describes the logical relationship among the public part of the ADT which are usually operations and the constants so when we talk about the specifications we actually mean what are the operations which are being supported by the ADT. We also cares about name of the operation, what input it will take, what output it will provide and we also identify what are the initial conditions which must be satisfied.
When the operations start executing if you also care about the post condition requirement, i.e. after execution of this operation what things must be satisfied. It all comes under specification part. For ex. In PUSH operation of a stack, precondition may be to check that TOP < StackSize, similarly postcondition ensures that TOP must be incremented after successful operation.
Design deals with the structure, which refers how all the operations which are defined inside the ADT and other a constant variable which is actually required to make that entity workable or provides its meaning. We need to identify and bind all the things that come under the design.
In ADT architecture we actually have two things, the operations which are defined inside ADT and the structure i.e. how we are going to bind all the operations together.
ADT are of many kinds you can just see some names mentioned here like list, trees, stacks, queues. These are some which are frequently used as a data structures for solving different problems. We have categorized these into two part known as standard ADT and non-standard or complex ADT. Basic difference between the two is that in standard ADT whatever structure is defined in design time will be used as it is till the final implementation.
In non-standard or complex ADT you might be defining at a design time and at the implementation time you may be un-wrapping this ADT to use it further. In this type of ADT, we define ADTs at the design time for getting some logical advantage, i.e. in some cases to simplify the things at a design time we frame ADT to get some logical advantage like to simplify the analysis of the correctness of the algorithm.
To summarize, ADT is an abstract data type and it’s a collection of similar kind of objects like we are defining as a class. Therefore, if it is a type then it’s a collection of instances, if the ADT is a set then it’s a collection of element, if ADT is a class then it’s a collection of object. It basically consists of the data structure declaration and the operation which are defined on this data structure.