Analysing means to find the performance of an algorithm which helps us to compare different algorithms which are available for any given problem.
This lecture we will be focusing on some very fundamentals which are required to analyse any algorithm. We will also discuss some of the basic mathematical notations and mathematical equations that are used frequently.
when we talk about solving a problem using a computer then there are defined steps or you can say it’s a kind of different stages one has to undergo to solve any problem using computers.
Let’s assume we are having some problem in hand, in order to solve it you need to look for the strategy and writes the algorithm. In the algorithm, we talk about input and output. Then comes the analysis of proposed solution (i.e. algorithm).
When you talk about the analysis of algorithm, we are basically concerned with three things
- to find the cost of the algorithm
- to test the optimality
- ensure correctness
cost of the algorithm – here to find out the time and space complexity, it means our intention is to find out how much time will be required to execute the given algorithm or we are interested to know how much memory will be required to run the given algorithm.
optimality here we look for the scope of improvement in the performance of the algorithm so in optimality our objective is to find out or to elaborate more about the given algorithm so that the performance can be improved. In this step basically we are looking for different strategies which are possible to make the performance better. Also we are looking for different data structures which can be used with the algorithm to improve the performance.
correctness – here our objective is to verify the correctness of the procedures that is being used in the algorithm. We need to ensure that the preconditions are satisfied then the post condition will be true.
Generally analysing algorithms means that these three things need to be done but most of the time we are mainly focusing on to find the cost (time and space complexity) of the given algorithm.
Cost of algorithm is basically defines the time requirement and the space requirement. Cost basically categorized into three cases we call it best case, average case and the worst case. There are certain notations to represent these cases, they are referred as asymptotic notations.
best case is represented by symbol omega, average case by symbol theta and the worst case is represented by big O.
best case is a special scenario or a special set of input for which the cost is minimum, for a defined set of input when the cost is minimum.
average case is a scenario that actually as the name reflect average case. It basically give you the averaging of the best and worst case. Evaluating the average case is not always possible because it’s not possible in all scenarios to get all kinds of input that are possible. To find out the average case you need to find all variations of input, so we are not interested most of the time in average case
worst case will be used to find out the maximum effort required so it represent the maximum cost that is required to execute the given algorithm and most of the time we always prefer to compute.
You plan for a budget when you do any task, it is just to find out how much expenses would be incurred to execute a particular plan, so when you do budget planning you always find out all the cost which are actually the visible expenses which are tangible.
You also allocating some funds for some invisible expenses you are predicting that there might be some scenario or you can say it’s called risk analysis.
You always do some kind of risk analysis; you always identify that there may be some scenarios that something may happen and it will also incur some cost. Hence, it should also be included in the budget planning. Therefore, in budget planning actually we are finding the cost that will be maximum or you can say the maximum amount that will be required to execute that plan.
Similarly, when we talk about the worst case, it represents the maximum effort or the maximum cost that will be required to execute the algorithm. Generally, we are interested to find cost in worst scenario because it’s a kind of guarantee it ensures, the guarantee that the algorithm will require at most these many resources.
Resources may be used in terms of time, in terms of memory, therefore, Cost analysis is done in terms of time requirement and the memory requirement. When we say time requirement, it means amount of effort required or amount of work done to execute all statements of the algorithms.
Why we are interested to find out the efficiency of an algorithm?
You may realize when you come across any problem or task, there might exists many different algorithms to solve a same problem/task. So how can we find out which particular method is good for us. There exist no single algorithms that is said to be the best algorithms/method for any problem in every scenario.
Every problem is defined with some constraints, to find efficient algorithm on the basis of the constraints, we have to
- understand the given problem
- Identify the constraints associated with the problem
- Identify the various ways (different algorithms) to solve the given problem
- Recognize which algorithm is suitable in context of the problem constraints.
For ex. If a series of numbers are to be sorted, then we have many sorting algorithms exist to solve this problem. But you may realize that for a particular scenario (constraint) the radix sort is considered best while in other scenario heap sort is good, whereas in some scenario merge sort is good likewise all existing sorting algorithms may be good with different constraints associated with the problem. Here we can’t claim that Quick sort would be best for sorting in all type of scenarios (constraints) Suitability of any algorithm for a given problem depends on the nature of the input, the nature of the problem, constraints, required output etc. for example, if your data is sorted and you are looking for the smallest element then you are not going to apply the binary search though, binary search is assumed to be a faster than linear search. In this case, data is already sorted, hence linear search would be good.
Mathematical model of computation – Good or bad algorithm for any problem mainly depends on the nature of the input and the associated constraints. It is to note that amount of work done is independent of the computer programming language or the programmers coding skills.
Generally, analysis of any algorithm is done using mathematical model of computation, (refer chapter mathematical model of computation). This model is required because we cannot compare two algorithms running on two different computers of different configuration, one computer is a very fast machine having a latest processor, good size RAM, while another computer is using a very old processor and not having a good amount of RAM. It’s obvious that when we run the algorithm on these machines, we will find a very different performance. This is not a good comparison, for a meaningful comparison we are setting aside all these parameters like configuration of the computers, programming language and other implementation details that may be affecting to the performance of the algorithm.
We simply consider input size on the mathematical model of the computation. Analysis basically depends on the size of the input that we are providing to the algorithms. the basic approach of doing this job is to
- to identify the basic operations present in the algorithm, simple basic operations are like comparing the two elements, adding the two elements, shifting element from one cpu register to other cpu register etc.
- to count the number of basic operations in the algorithm. For ex., if loop is used, then we need to count that how many times that operation is used inside the loop.
when we say best case, average case, or worst case this actually depends on the nature of input we are providing it. One thing to understand that the nature of input is varying for different kind of algorithm. It is not same for all kind of algorithm. for example, sorted data may be good for one kind of algorithm but it may not be good for other kind of algorithm. So, we need to check the context of the algorithm and then we will see what is the nature of the input that affects the behaviour of algorithm.
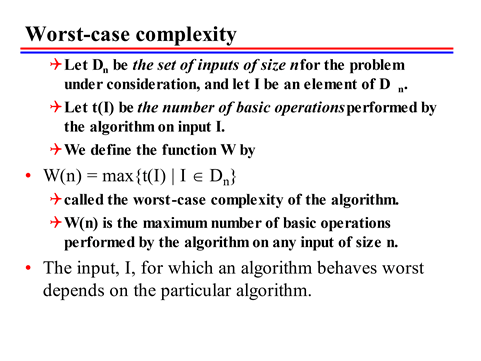
Worst case complexity – As already mentioned that most of the time we are interested to find out the worst case complexity, alternately we are interested to know the maximum amount of effort required or maximum amount of time required to solve problem (or run that algorithm). We need to formulate some notation or devise some mechanism to represent this worst-case scenario.
Time Complexity – Let Dn with a set of inputs of size n for the problem under consideration and let I be the element of Dn, let’s say these are the i1 i2 i3 …… iN and let’s say each input is of size 4, so let’s say i1 is represented as (1, 2, 3, 4). so we have a set Dn which is a collection of inputs and input is of defined size. Let t(i) be the number of basic operations performed by the algorithm on input i. Amount of time required to run the algorithm using input i1. let’s say t1, for input i2 time is t2, similarly, when we pass input i3 time is t3. Because input nature is different and when we provide this input to the algorithm, it will take different times.
Let us define the function w by wn equals to maximum of ti (where i is an element of Dn) i.e. out of all the possible execution time whichever is maximum will be the worst time complexity.
In case of sorting problems, basic operation is comparison operation (to compare two elements to determine its position). With different set of inputs, the amount of effort required would be different to search any element in a list. If element exist as first element, it requires minimum effort in other case if element not exist or exist at last position then it will require maximum effort to get the solution. If the list size in n then it requires maximum n comparison to get the result. We need to understand that a particular input may be a best case for any algorithm but not the best case for other algorithm.
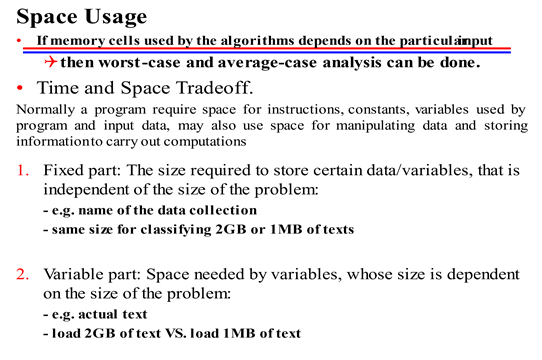
Spcae Complexity – Next is the space usage to execute any algorithm. we also find the cost in terms of the space, which means how much memory cell will be required to run the algorithm. For the different size of input, you need a different memory and then you are going to find the worst case. (i.e., maximum memory cells required)
There may be many algorithms where you will find that whatever is the size of the input it will not affect the memory requirement. For ex. either you pass 10 elements, or you pass 100 elements or you pass 2000 elements the memory requirement will be same, it mean that it will require the constant amount of memory and independent of amount size.
Why we require the space? space is required for various reasons,
- it is required for executing the instructions that you have defined in the algorithm
- you may be using some constant but that will also occupy some space
- you may be using some variables that will be used in the algorithm so you need a space for variables
- there may be some data that is need to be passed to the algorithm and
- you may be doing some internal computation; you are manipulating the data and then you need to store these intermediate results.
It all depends on how you are using your data, what other things you’re providing in the algorithm. Though we always interested to find the space and time complexity but our main emphasis will be on finding the time complexity. As our technology is advancing you may have realized that the cost of the memory is becoming cheaper. For ex, 10 years back the cost of memory is huge but as the time passes and the technology is advancing the memory is becoming very cheap. Therefore, our main concern is the time factor of any algorithm. Keeping this in mind, we do the trade-off means you need to compromise one of the factors. It’s a general phenomenon that algorithms which are very fast take more space. So depending on our requirement and the requirement of the application we decide our priority and do a trade-off to compromise on one of the factors.
when we talk about the space requirement, certain part of the input is considered as a fixed part that will require a fixed amount of memory and some part is called variable part means this amount is keep on changing depending on the nature of the input. fixed part is the size required to store certain data variables that is independent of the size of the problem, it means fixed part refers to the space requirement which is independent of the input size. For ex. name of data collection, the identity of any constant variables.