Mathematical model is a kind of theoretical computer which is used to analyse the algorithm. It basically serves as a framework for algorithmic analysis.
In real computers (the machines that we use to execute our program), if you write a very simple statement to add the two numbers say ( a = b + c), if you look at instruction set to execute this kind of statement, it is little complex execution. Here
- first you have to load b into some register let’s say register one
- then you are going to load c into register two
- then you are going to add the values stored in these two registers and then placing it in some third register and then assigning the value of third register to a
Why we study this model for the analysis of algorithm
in the mathematical model, we have some defined instructions set that are very straightforward, very simple. The question arises is that why it is required to study mathematical model and why we always talk of mathematical model to analyse algorithm.
In the real computers we have a program and they are developed using any programming language when we talk about mathematical model, it only has a meaning when we talk about algorithm. Therefore, the key entity that runs on this model is the algorithm.
If you analyse your algorithm by running on different computers then there are many different factors that can affect the performance of your algorithm because these computers may have designed using different architecture, different instruction set. other factors that affect the performance includes processor, ram, programming language, efficiency of the programmer, etc. There are many other components that can affect the overall execution of any program.
Here we are not comparing the program performance but our objective is to compare or evaluate the performance of an algorithm. Here we need a model that should be independent of all these factors which can affect its performance. Hence, mathematical model is a very simple critical computing machine which is based on a very simple instruction set. The core objective of this model is to evaluate the effort required for every step which is defined in the algorithm.
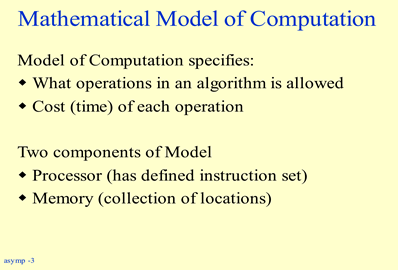
Mathematical model basically specifies two things
- the types of operation and
- the cost of operation
it basically specifies that what kind of operations are allowed in the algorithm to be executed and what is the cost of each operation.
The entire architecture is built on two component, processor and memory.
Processor like in our real computers has a instruction set. we need to understand that how this instruction set is defined so that we can evaluate each step which is mentioned in the algorithm.
Memory is just a collection of location and these locations are assumed to be array of memory spaces which is recognized by its address. Accessing any location with the help of address may be inconvenient so this model also allows us to declare variables because accessing the location using variable is quite easy for the user. it also allow to use the primitive data type like we are using in normal computer programs using the programming languages; Hence mathematical model is much more simplified than the real machines.
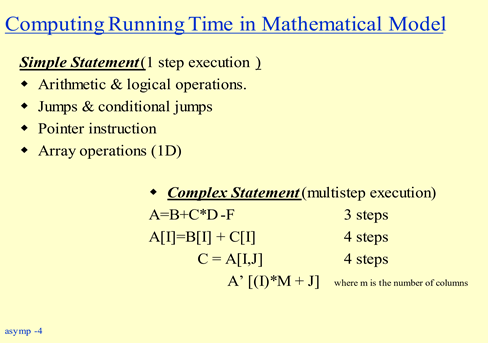
Let’s start with a very simple statement that how they are evaluated so here our objective is to find out the cost of each statement that we are using so here we evaluate in terms of step. We can say that the statement will require one, two, three or more steps as a unit of measurement; it actually signifies the cost of that particular statement.
We’ll start with the very simple statements like arithmetic and logical operations, jumps and conditional jumps, pointer instructions, one-dimensional array operations. These all are simple statement and requires only one step execution. There is no cost if you assign any constant to the variable for example a=2 or a=b (there is no cost defined for such statements) For the statement like a=b+c , if there is any operator involved in the expression, then it will require step execution to perform this operation. In this case one operator (+) is used so cost is 1-step. Similarly if you are using jumps and conditional jumps then also it is a simple statement. Statements using if-condition like a>b or b>8 or c<=m, this kind of statement is also said to be one step execution. Pointer instructions b= *c or c=&b are also one step execution. Likewise any statement referring to one dimension array like
a[1]=6 , a[9]=b or c=j[2] are also one step execution.
Total cost of any algorithm is to identify the cost of each statement (in terms of steps) and then add the cost of all the statements in the algorithm.
Let’s see the cost of some more complex statement (not a single step) which requires multi-step execution. For example a=b+c*d-e as three operators are used in the expression, it is a three step execution. Similarly, if there is a statement like a[i]=b[j]+c[j], herewe see one operator and three one-dimensional array in the expression so the cost is four-step execution
a[i]=b[j]+c[j]. executes in the following sequence l=c[j] m=b[j] k=l+m a[i]=k
The cost of each usage two dimensional array is 4 steps, i.e. any 2 dimension notation of type a[i,j] or a[i][j] will cost 4-steps
So the expression j=a[i] + f + c[i][m] will cost 7 steps
Two-dimension is basically a logical representation, actually everything is a linear allocation in the actual physical memory.
for example , there is an array whose dimension is A[ ]2×4, means it has two rows and four column. although we are looking it as a two dimensional but actually in a physical memory these elements are placed continuously in such a way from zero to seventh index. When you want to access any of the element normally in the program, let’s see how the mapping is done
The expression C= a[i][j] will be internally represented as C= A’ [ i*m + j ]
where i and j represent required row and column respectively, and m is a number of columns in given array
so, when any algorithm is given to you just need to identify that what is the cost of each statement and then just add all the cost that gives the entire cost of the algorithm. Here the entire scenario is independent of any programming language, cpu structure, ram-size, etc.