Max-Heapify – It is an operation used in the context of binary heaps, specifically in max-heaps. A max-heap is a complete binary tree in which the value of each node is greater than or equal to the values of its children. Max-Heapify is responsible for maintaining the max-heap property by fixing a single violation, where a node may have a value smaller than one or both of its children.
The Max-Heapify operation takes as input a heap and an index indicating the position of the node that may violate the max-heap property. It then adjusts the values of the nodes in the subtree rooted at that index to ensure that the max-heap property is satisfied.
The Algorithm is as follows :
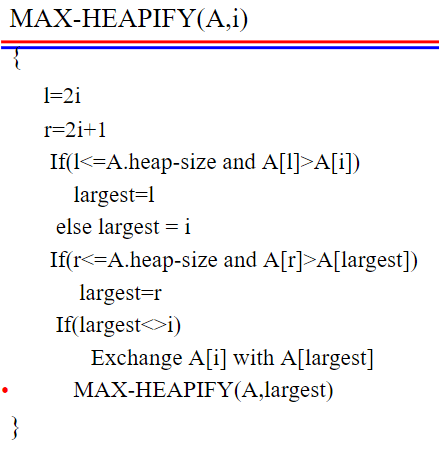
Here is a step-by-step explanation of the Max-Heapify operation:
- Let the index of the node be i.
- Compare the value of node i with the values of its left and right children (if they exist).
- Find the largest value among node i, its left child (if it exists), and its right child (if it exists). Let’s say the largest value belongs to one of the children.
- If the largest value belongs to the left child, swap the values of node i and its left child. Update i to be the index of the left child.
- If the largest value belongs to the right child, swap the values of node i and its right child. Update i to be the index of the right child.
- Repeat steps 2-5 until node i is larger than both its children or until it becomes a leaf node (has no children).
The purpose of the Max-Heapify operation is to ensure that the largest element (the root) is at the top of the heap. By repeatedly applying Max-Heapify to nodes starting from the bottom and working upwards, the entire heap can be transformed into a valid max-heap.
Max-Heapify has a time complexity of O(log n), where n is the total number of elements in the heap. This complexity arises because the operation involves traversing the heap from top to bottom, and the height of a heap is logarithmic with respect to the number of elements.