loop invariants are powerful tools for understanding, verifying, and developing correct loop-based algorithms. By expressing the key properties that hold throughout the loop’s execution, they provide valuable insights into the loop’s behavior and help to ensure its correctness. Loop invariants are conditions or assertions about a program’s variables that are guaranteed to be true before and after each iteration of a loop. They play a crucial role in:
Understanding loop behavior: Loop invariants help to clearly express the purpose and progress of a loop, making the code easier to understand and reason about.
Proving correctness: Loop invariants are essential in formal program verification techniques, like the Floyd-Hoare approach, to mathematically prove that a loop achieves its intended goal.
Writing correct code: Thinking explicitly about loop invariants during development helps to prevent errors and ensures that the loop operates as expected under all circumstances.


Key Points to remember
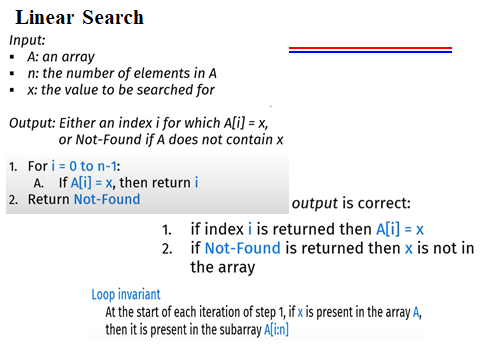
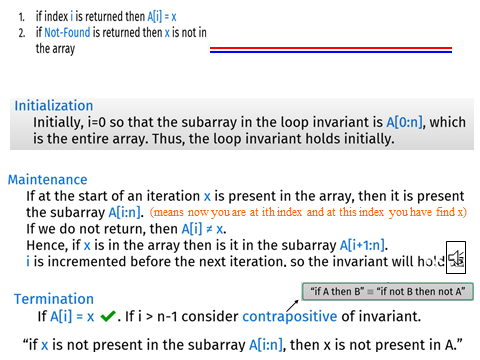
- A loop invariant must be true before the first iteration of the loop.
- If the loop invariant is true before an iteration, it must remain true after the iteration.
- The loop invariant often captures some partial progress towards the loop’s ultimate goal.
- Loop invariants are typically expressed as logical predicates involving the loop’s variables

One thought on “Understanding Loop Invariants”