A B-tree (Balanced Tree) is a self-balancing tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows for efficient insertion, deletion, and search operations. It is particularly useful in databases and file systems where large amounts of data need to be stored and retrieved efficiently. The key feature of a B-tree is its ability to keep the tree balanced during insertions and deletions, ensuring relatively uniform height and optimal performance.
B-trees are a crucial data structure due to their ability to efficiently organize and manage large datasets in a balanced manner. Their logarithmic height ensures fast search operations, making them well-suited for applications requiring quick access to data, such as databases and file systems. The self-balancing property allows B-trees to adapt to changes in dataset size, maintaining a consistent performance for insertions and deletions. This adaptability is particularly valuable in dynamic environments where data is frequently updated.
Moreover, B-trees optimize disk I/O operations, making them ideal for scenarios where data is stored on disk. B Tree is a specialized m-way tree that can be widely used for disk access. A B-Tree of order m can have at most m-1 keys and m children. One of the main reason of using B tree is its capability to store large number of keys in a single node and large key values by keeping the height of the tree relatively small. A B tree of order m contains all the properties of an M way tree.
In addition, it contains the following properties.
- Every node in a B-Tree contains at most m children.
- Every node in a B-Tree except the root node and the leaf node contain at least m/2 children.
- The root nodes must have at least 2 child nodes.
- All leaf nodes must be at the same level.
- It is not necessary that, all the nodes contain the same number of children but, each node must have m/2 number of child nodes.
Inserting a Node in a B tree
Insertions are done at the leaf node level. Steps to insert an item into B Tree
- Traverse the B Tree in order to find the appropriate leaf node at which the node can be inserted.
- If the leaf node contain less than m-1 keys then insert the element in the increasing order.
- Else, if the leaf node contains m-1 keys, then follow the following steps.
- Insert the new element in the increasing order of elements.
- Split the node into the two nodes at the median.
- Push the median element upto its parent node.
- If the parent node also contain m-1 number of keys, then split it too by following the same steps.
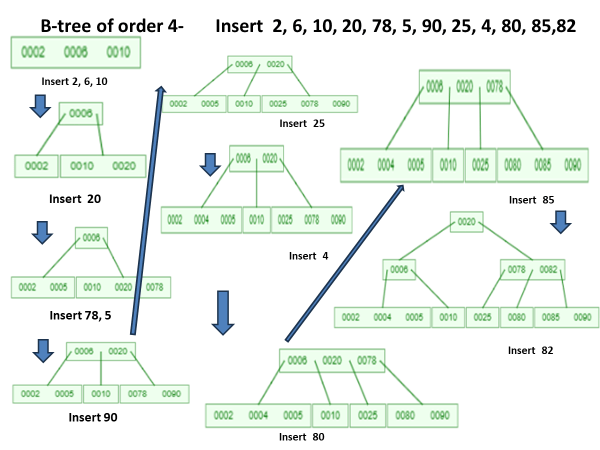
Example 1 B-tree of order 4-
Insert 2, 6, 10, 20, 78, 5, 90, 25, 4, 80, 85,82
Eexample 2 – B-tree of order 3-
Insert 12, 16, 10, 20, 78, 15, 90, 25, 14, 80, 85,82

Deleting a node in a B Tree
Deletion is also performed at the leaf nodes. The node to be deleted can either be a leaf node or an internal node. Algorithm – to delete a node from a B tree as follows
•Locate the leaf node.
•If there are m/2 keys in the leaf node then delete the desired key from the node.
•If the leaf node doesn’t contain m/2 keys then complete the keys by taking the element from right or left sibling.
•If the left sibling contains m/2 elements then push its largest element up to its parent and move the intervening element down to the node where the key is deleted.
•If the right sibling contains m/2 elements then push its smallest element up to the parent and move intervening element down to the node where the key is deleted.
•If neither of the sibling contain m/2 elements then create a new leaf node by joining two leaf nodes and the intervening element of the parent node.
•If parent is left with less than m/2 nodes then, apply the above process on the parent too.
•If the node which is to be deleted is an internal node, then replace the node with its in-order successor or predecessor.

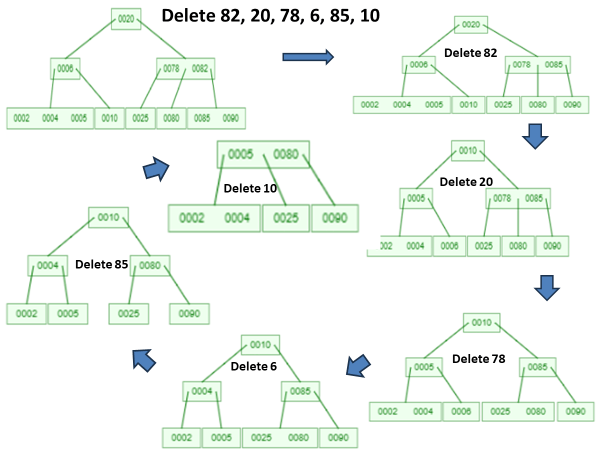
Example Btree of order 4 -Delete 82, 20, 78, 6, 85, 10
Example 2 – Btree of order 3 -Delete 25, 15, 32, 64, 12

Watch videos of this topic at the link below
[Click the following links to watch the video]