B+ trees are a specialized form of B-tree that address specific needs in database systems and file storage. One key advantage of B+ trees is their efficient support for range queries and sequential access. In a B+ tree, all the keys are stored in the leaf nodes in a sorted order, and these leaf nodes are linked together. This design facilitates quick retrieval of ranges of keys, making B+ trees particularly well-suited for applications where sequential access and range queries are common, such as in database systems.
Another important feature of B+ trees is their ability to provide a clear distinction between the structure of the tree (internal nodes) and the actual data (stored in leaf nodes). This separation simplifies the management of the tree structure and enhances the efficiency of search operations. Additionally, B+ trees are commonly used in scenarios where data needs to be stored on disk, as their characteristics lead to more efficient disk I/O operations.
•In B Tree, Keys and records both can be stored in the internal as well as leaf nodes. Whereas, in B+ tree, records (data) can only be stored on the leaf nodes while internal nodes can only store the key values.
•The leaf nodes of a B+ tree are linked together in the form of a singly linked lists to make the search queries more efficient.
•B+ Tree are used to store the large amount of data which can not be stored in the main memory.
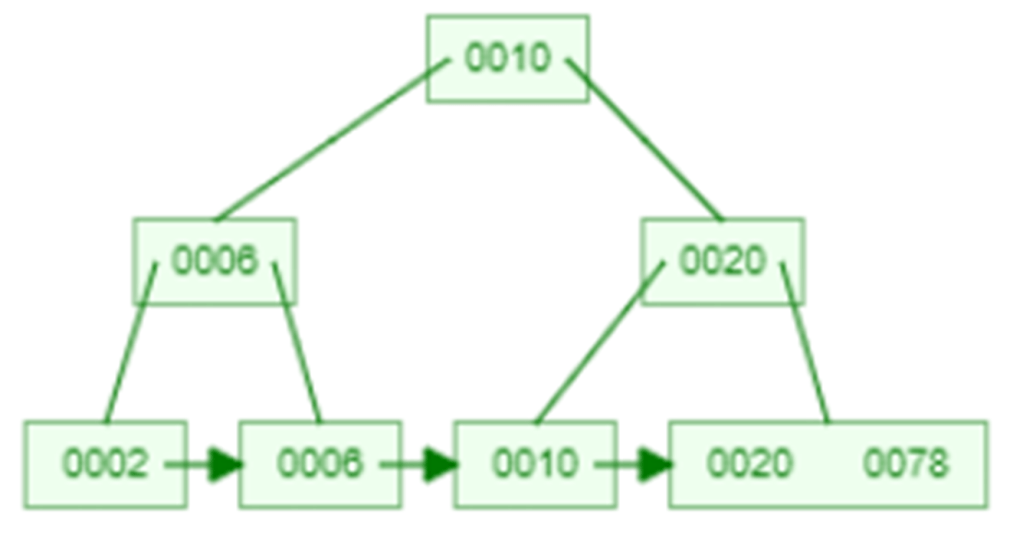
The internal nodes of B+ tree are often called index nodes. A B+ tree of order 3 is shown in the following figure
Insertion in B+ Tree
Step 1: Insert the new node as a leaf node
Step 2: If the leaf doesn’t have required space, split the node and copy the middle node to the next index node.
Step 3: If the index node doesn’t have required space, split the node and copy the middle element to the next index page.
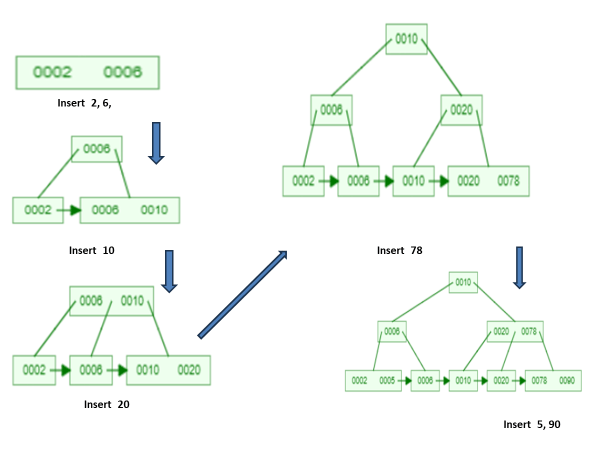
Example-1 : In B+ Tree of order 3, Insert 2, 6, 10, 20, 78, 5, 90
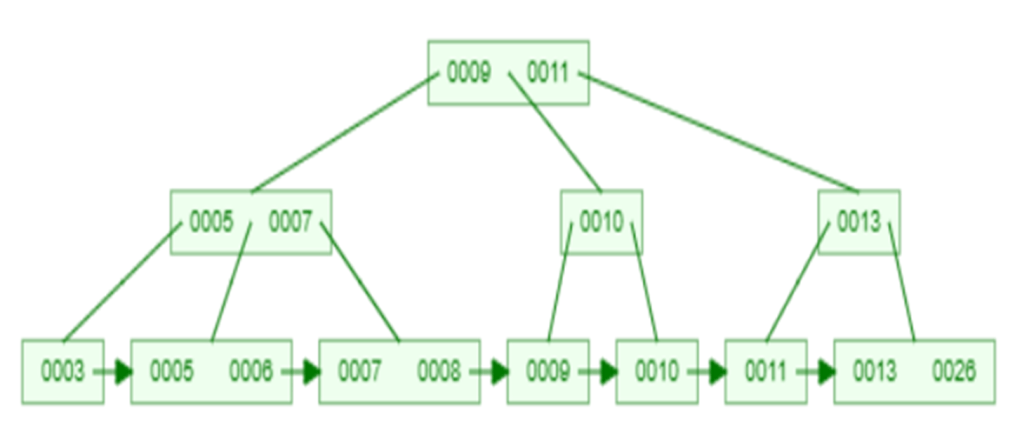
Example-2 : In B+ Tree of order 3, Insert 10, 9, 8, 11, 7, 5, 6, 26, 3, 13
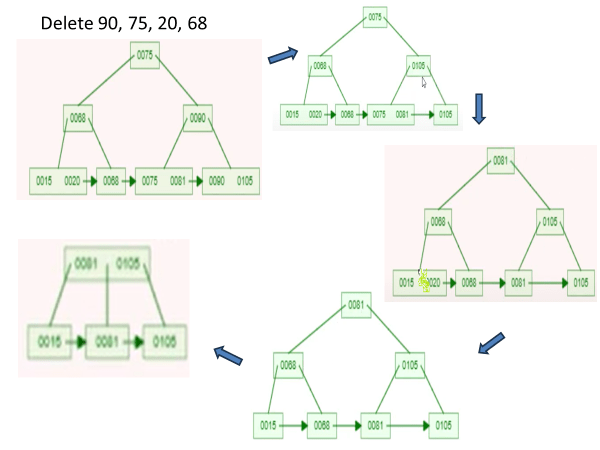
Deletion in B+ Tree
Step-1 Start at the root and traverse the tree to find the leaf node where the key is located.
Step-2 Once the leaf node containing the key is found, remove the key from the node. If the deletion causes the node to have too few keys, consider borrowing a key from a neighboring leaf node or merging with a neighbor to maintain balance.
Step-3 If the deletion results in changes to the structure of the tree (e.g., merging nodes), update the parent nodes accordingly. This may involve adjusting keys in the parent nodes and recursively checking for balance.
Step-4 Ensure that the B+ tree remains balanced after the deletion. If a node becomes too empty, consider borrowing a key from a neighboring node, merging with a neighbor, or redistributing keys to maintain a balanced structure.
Step-5 If pointers or links exist between leaf nodes (common in B+ trees), update these pointers to maintain the linked structure.
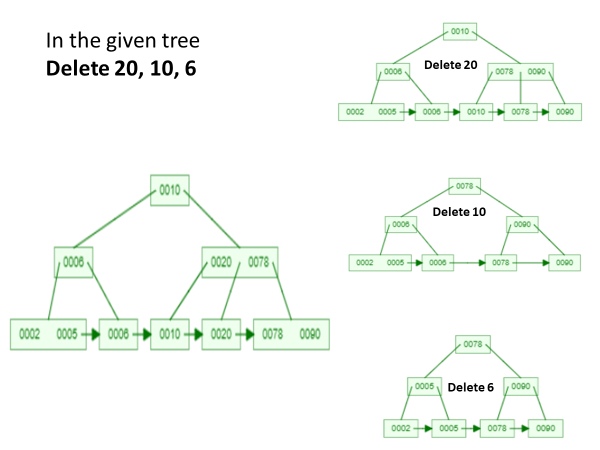
Example-1 : In B+ Tree of order 3, Delete 20, 10, 6
Example-2 : In B+ Tree of order 3, Delete 90, 75, 20, 68
Video Lectures on this topic can be found at following link