Inserting a node into a RB tree involves several steps to maintain the balance properties of the tree. Red-Black Trees are binary search trees with additional properties to ensure they remain balanced.
Here’s how you can insert a node into an RB tree:
- Insertion as in a Binary Search Tree (BST): First, insert the new node into the tree as if it were a regular Binary Search Tree (BST). Ensure the BST properties are maintained, where all nodes in the left subtree are less than the current node, and all nodes in the right subtree are greater than the current node.
- Color the New Node Red: Initially, the new node is colored red. This step preserves the Red-Black Tree’s property that all new nodes are red.
- Fix Violations:
- Check the Red-Black Tree properties and look for any violations that might have occurred during the insertion.
- There are several cases to consider and adjust based on the color of the new node, its parent, and its uncle (the sibling of the parent).
Here are the cases you may need to handle:
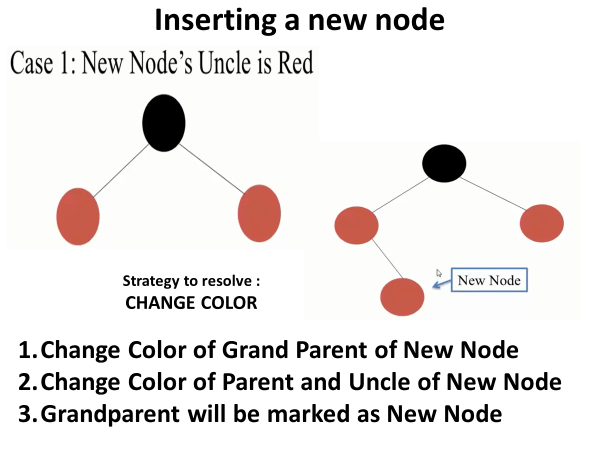
Case 1: If the parent of the new node is red, and the uncle is also red, then you need to recolor the parent and uncle nodes to black, and recolor the grandparent node to red. This action may propagate the problem upwards to the grandparent, so you may need to continue fixing violations at that level.
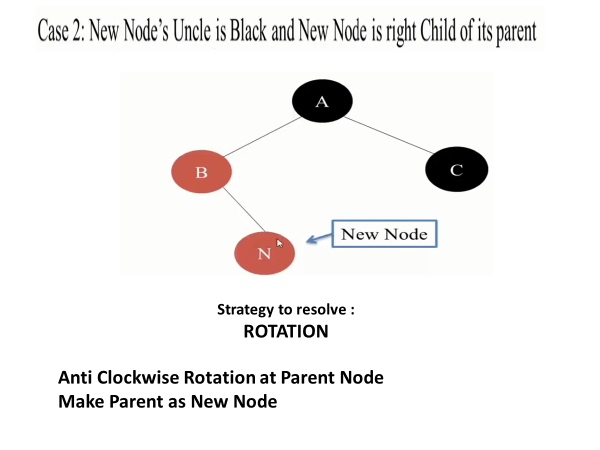
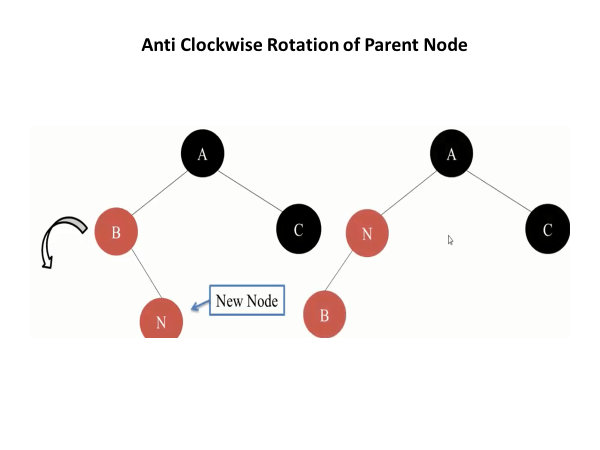
Case 2: If the parent is red, but the uncle is black (or null because a black node is assumed), and the new node is the left child of the right child (RL case) or the right child of the left child (LR case), you need to perform a rotation on the parent in the direction of the violation, making it a valid RR or LL case.
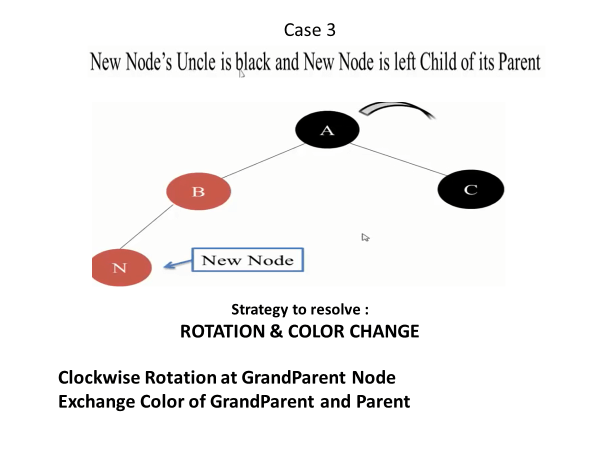
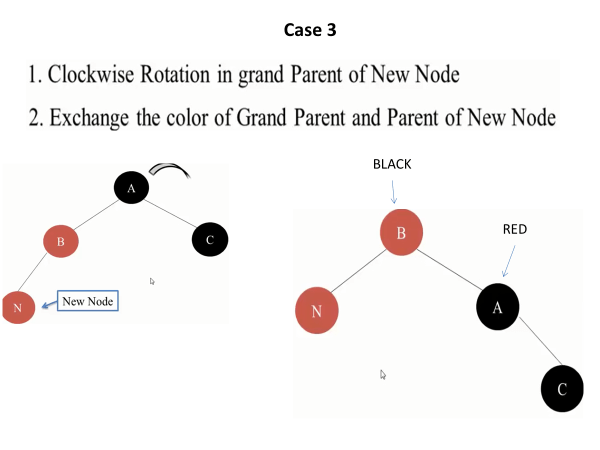
Case 3: If the parent is red, but the uncle is black, and the new node is the left child of the left child (LL case) or the right child of the right child (RR case), you need to recolor the parent to black, the grandparent to red, and perform a rotation on the grandparent in the opposite direction of the violation.
By following these steps, you can insert a node into a Red-Black Tree while maintaining its balance and satisfying the Red-Black Tree properties. The tree remains balanced with a maximum height of approximately 2*log2(n), where “n” is the number of nodes in the tree.