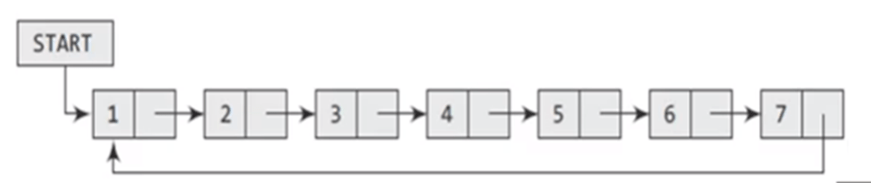
In a circular linked list, the last node contains a pointer to the first node of the list. While traversing a circular linked list, we can begin and traverse the list in forward direction until we reach the same node where we started
Implementing a Simple Circular Linked List
We use two classes: Node and List
Declare Node class for the nodes
- data: int-type data , next: a pointer to the next node in the list
To implement a circular singly linked list
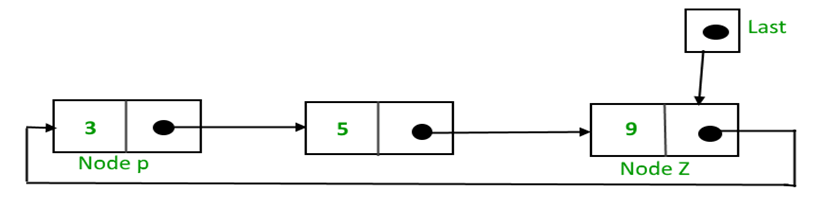
Take an external pointer named “last” that points to the last node of the list. last à next will point to the first node.
The pointer last points to node Z. last –> next points to node P.
Significance of Last pointer
The idea of pointer that points to the last node instead of the first node. In General, insertion of a node at the beginning or at the end, the whole list has to be traversed.
If we take a pointer to the last node, then in both cases there won’t be any need to traverse the whole list. (i.e. it takes constant time, irrespective of the length of the list)
Inserting a New Node in a Circular Linked List
Ther are 3 basic scenarios
Case 1: The new node is inserted at the beginning of the circular linked list.
Case 2: The new node is inserted at the end of the circular linked list.
Case 3: insertion somewhere in between the two nodes.
Case1 – Insertion at the Beginning
Steps to insert a Node at beginning:
- The first Node is the Head for any Linked List.
- When a new Linked List is instantiated, it just has the Head, which is Null.
- Else, the Head holds the pointer to the first Node of the List.
- When we want to add any Node at the front,
- we must make the head point to newly added node.
- Next pointer of newly added Node, must point to previous Head, whether it be NULL(in case of new List) or the pointer to the first Node of the List.
- The previous Node pointed by Head is now the second Node of Linked List, because the new Node is added at the front.
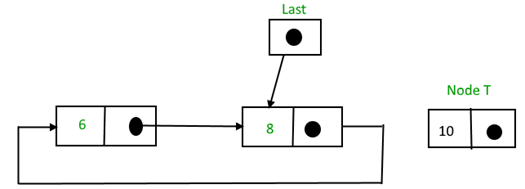
Case 2 -Insertion between the Nodes of Circular Linked List
Search for the node after which new node to be inserted, (say node with value 20)
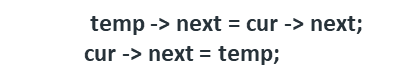
Alternatively, we can also use two pointers ( prev & cur ) as follows

Case 3 -Insertion at the End of Circular Linked List