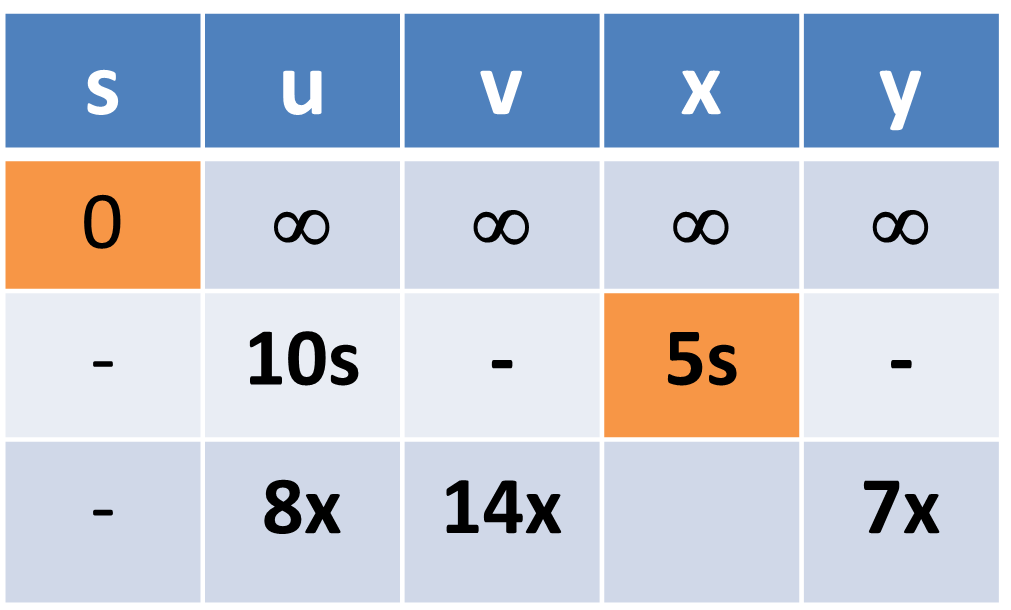Here are few examples that will help you to prepare for any Computer Algorithms Examination
Asymptotic Notations (Big-oh, Omega, Theta)
Solving Recurrence Equations (using recurrence tree & back-substitution)
Solving Recurrences using Masters theorem
Solving Heap Based Problems (heapify, build-heap, extract-max)
Sorting Based Problems (quick-sort, merge-sort, heap-sort, radix-sort)
Red Black Tree Operations
Order Statistics Tree & Interval Tree Operations (rank, k-th smallest)
Splay Tree Operations
Finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) (using Prims and Kruskal)
FInding Shortest Path (using Djikshtra and Bellman Fords)
Problem Solving using Greedy Approach (solving 0/1 and Fractional Knapsack)
Problem Solving using Dynamic Programming
Finding Pattern in Given String (using KMP and Boyers- Moore Algorithms)
Problems on Asymptotic Notations
Question : Find the O- notation for following functions. (Show the steps to evaluate value of c and no)
Solution : (click for video explanation)
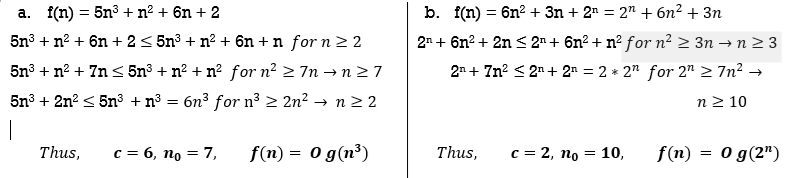
Question : Find the big omega- notation for following functions. (Show the steps)
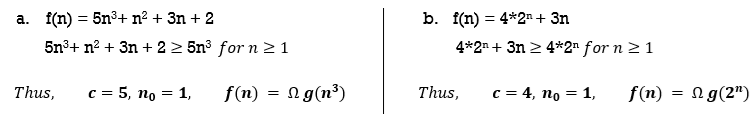
Question : Find the theta notation for following functions. (Show the steps)
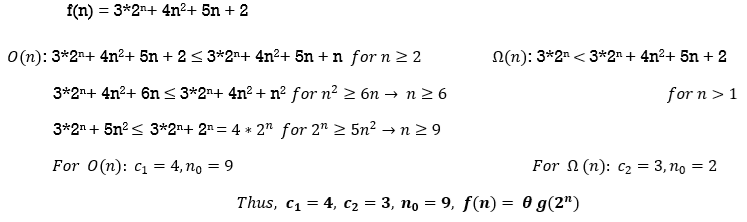
Question : Comment on the following (check bounds are correct or incorrect)
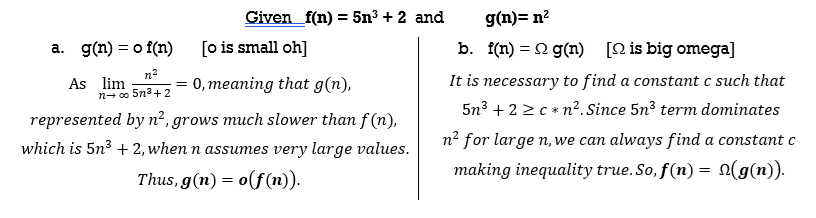
Problem on Recurrence Equations
Question : Solve following Recurrence using Back Substitution method
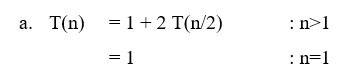
Solution : ( click for video explanation)

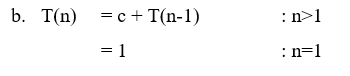
Solution : ( click for video explanation)

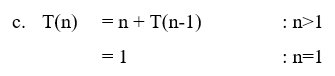
Solution :
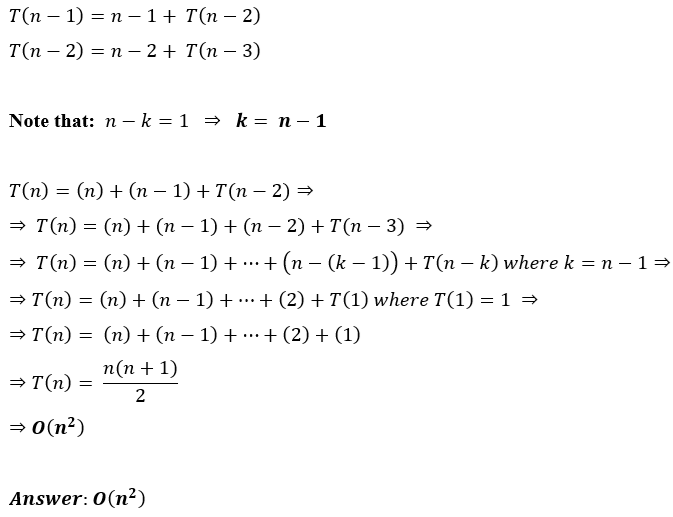
Question : : Solve following Recurrence using Recursive Tree method
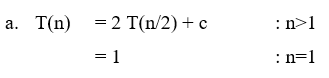
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
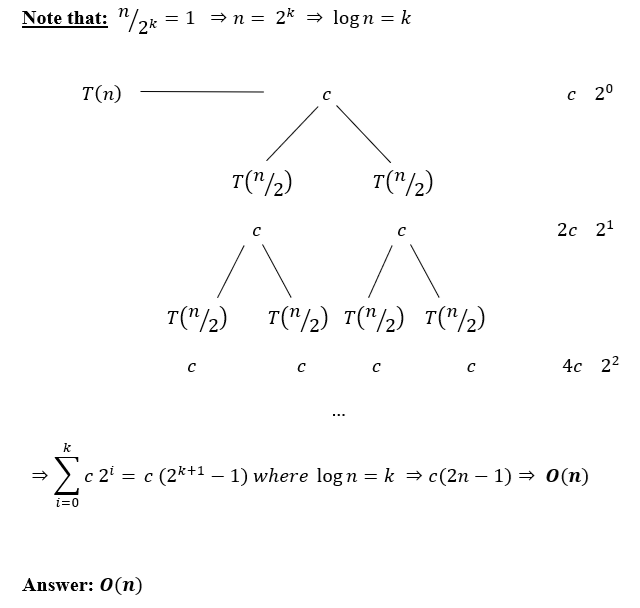
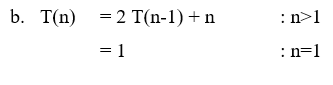
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
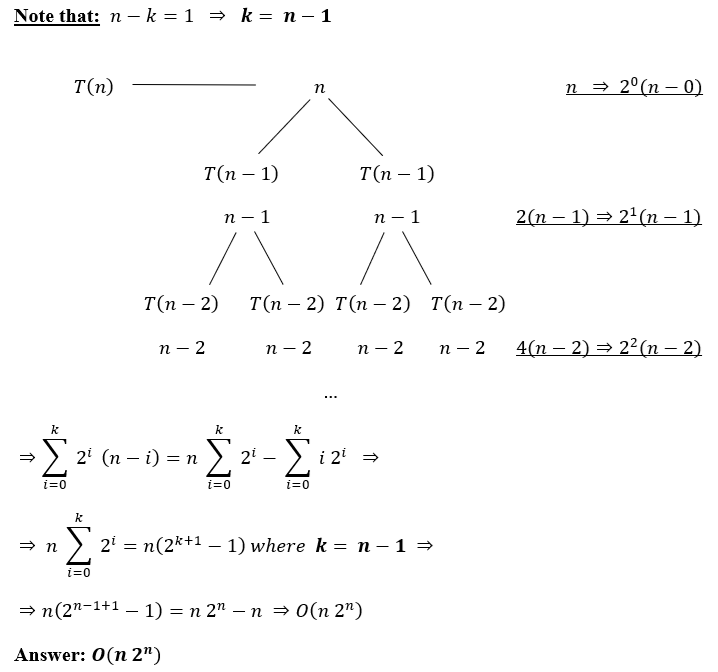
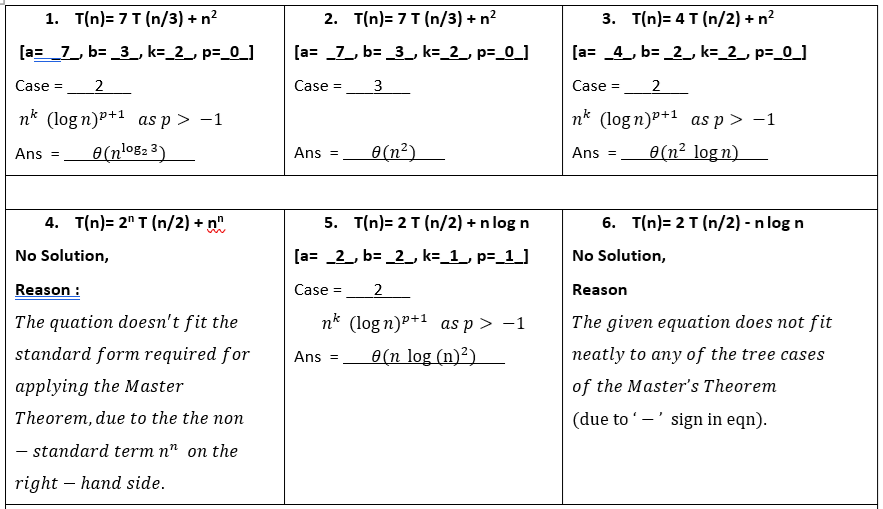
Probelms on Master’s Theorem
Question : Solving following Recurrence Equations using Masters Theorem
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
Problem on Heap
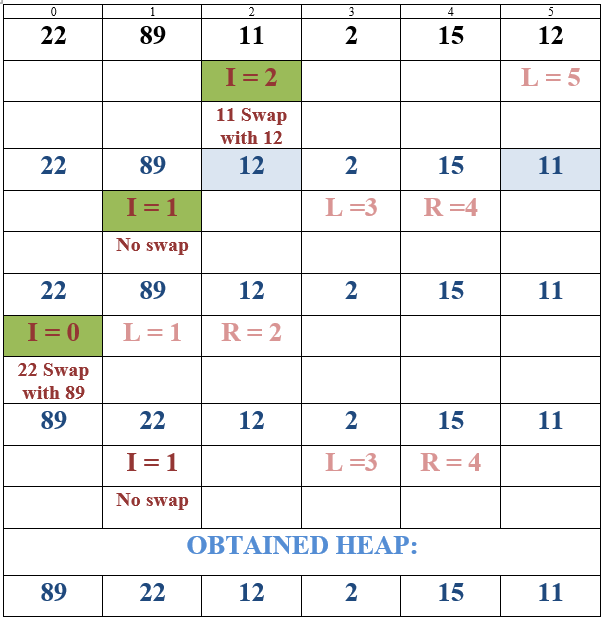
Question : Convert the following sequence to a Heap using Build Max Heap
22, 89, 11, 2, 15, 12
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
Execution STEPS
A = [22, 89, 11, 2, 15, 12]
Length(A) = 6
- MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 2) l = 5, r = 6 r does not exist. A[2] change with A[5].
- MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 1) l = 3, r = 4, nothing happens.
- MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 0) l = 1, r = 2, A[0] change with A[1].
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 1) l = 3, r = 4, nothing happens.
Question : Apply Build-Max-Heap on following tree
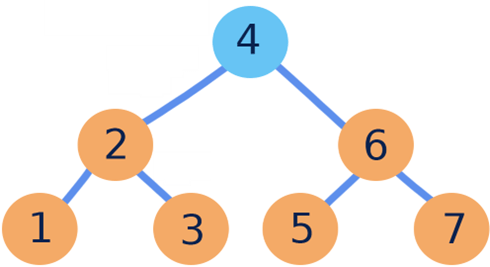
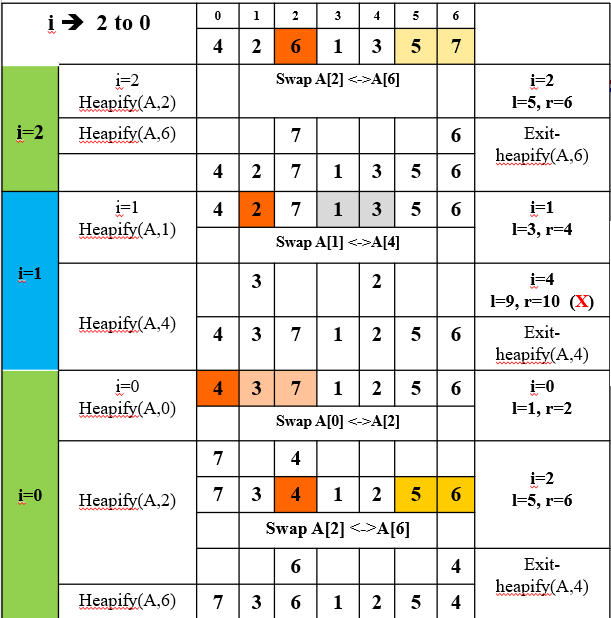
Question: Apply Max-Heapify (A,0) on following tree
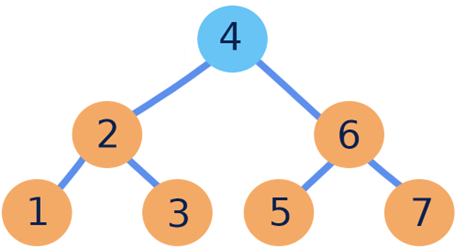
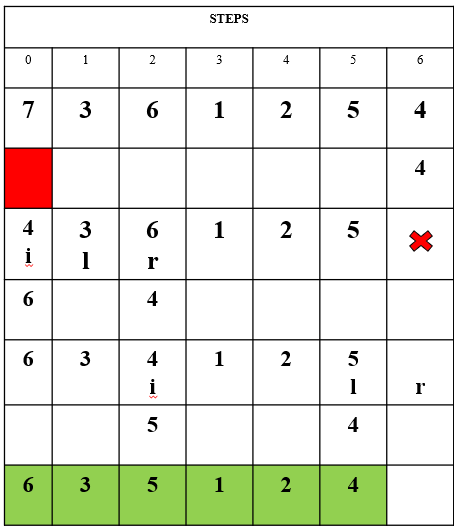
Question: Apply Heap-Extract-Max in the following heap
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 7 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
Solution
Problems on Sorting
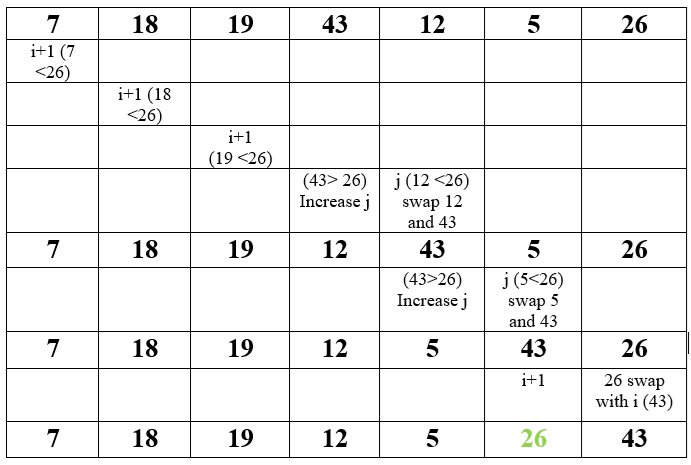
Question : Apply Quicksort Algorithm to sort the given sequence
7 18 19 43 12 5 26
Solution ( click for video explanation )
Following steps show only steps of PARTITION on the initial array
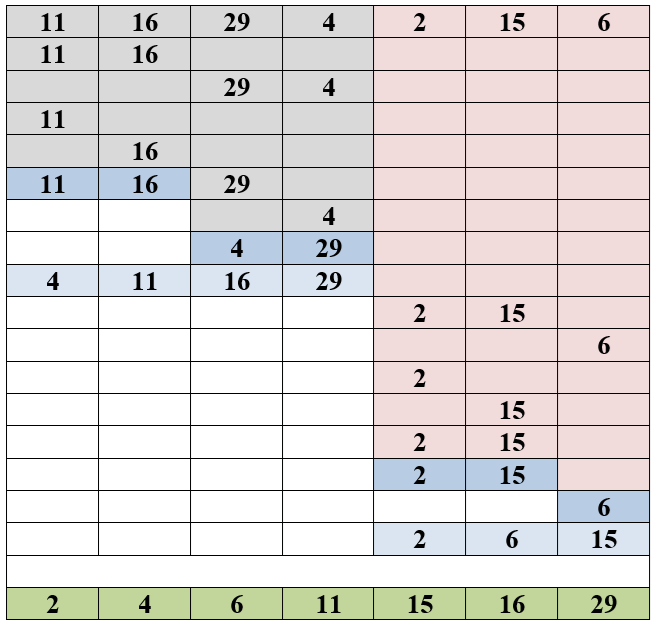
Question : Apply Merge sort Algorithm to sort the given sequence
11 16 29 4 2 15 6
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
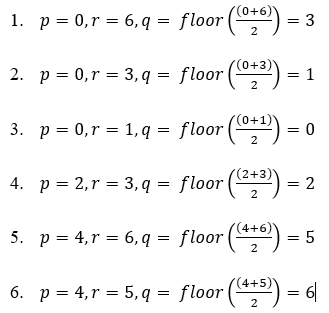
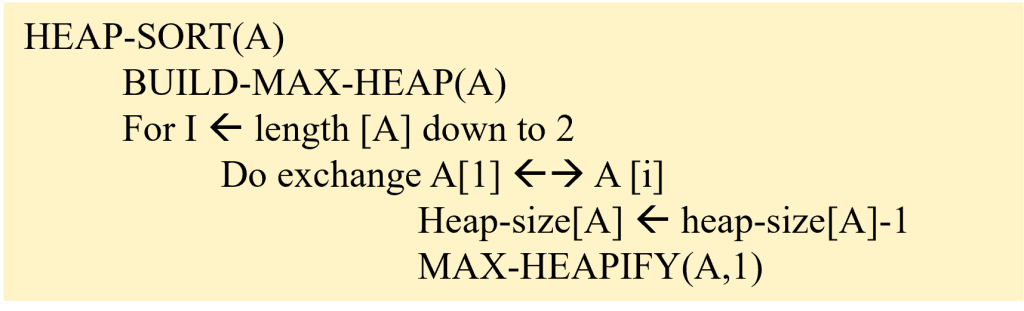
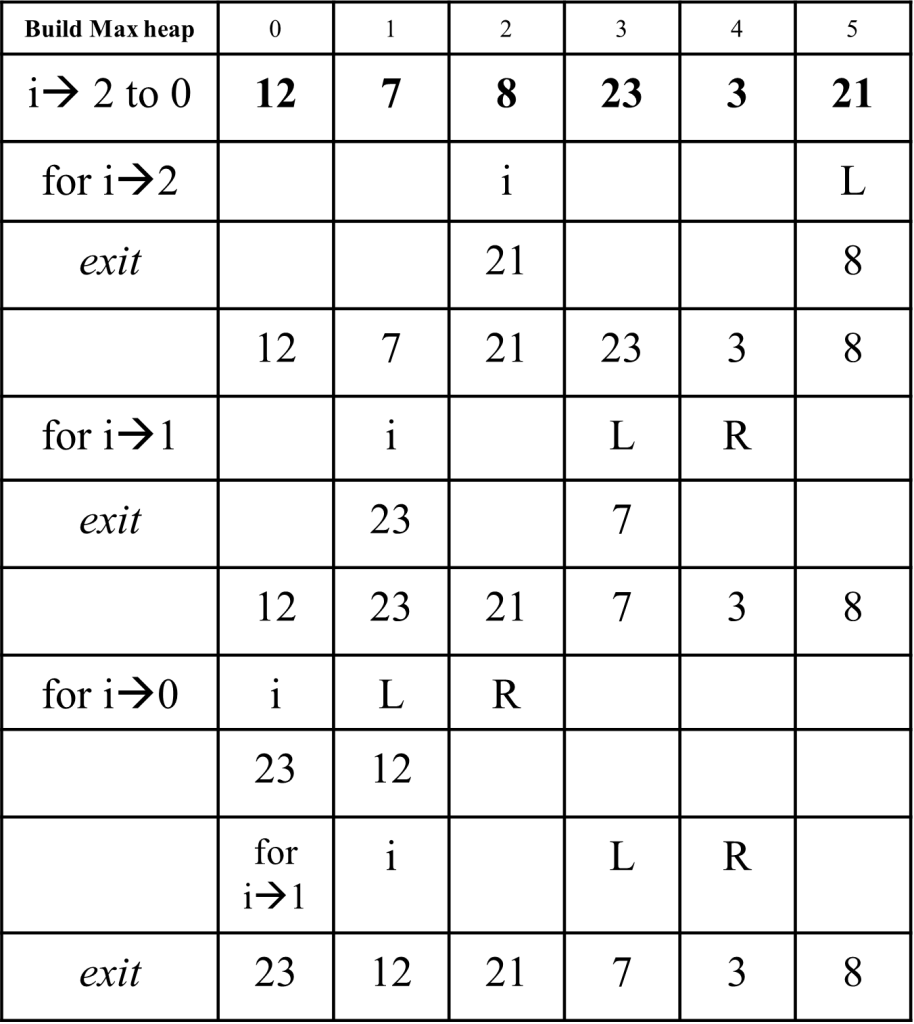
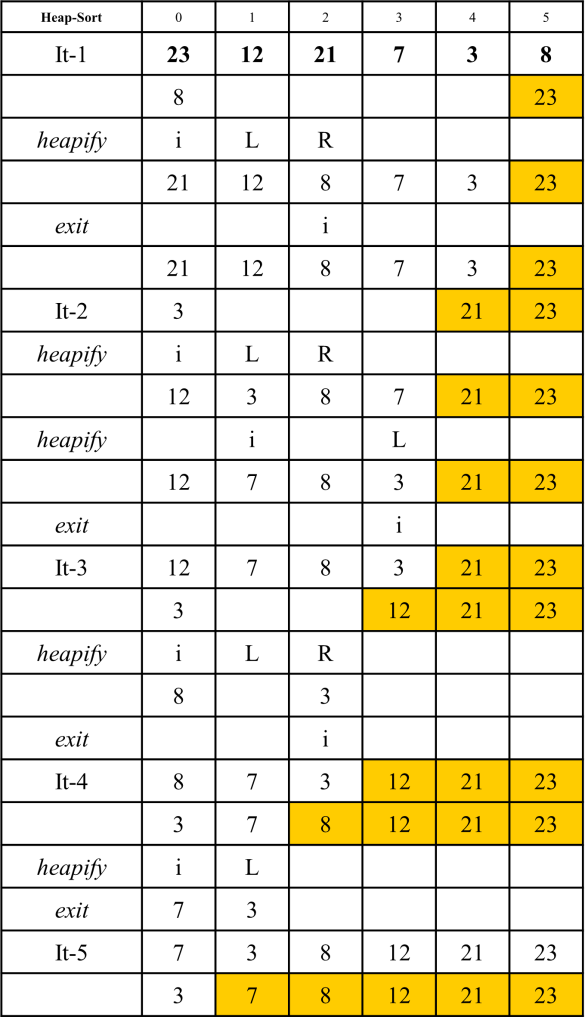
Question : Apply Heap sort Algorithm to sort the given sequence
12, 7, 8, 23, 3, 21
Solution : (click for video explanation)
Heap Sort requires the given sequence to be converted to heap, then the sorting is applied. Following are the algorithm used
Steps for converting Heap and then Heap-sort is shown below
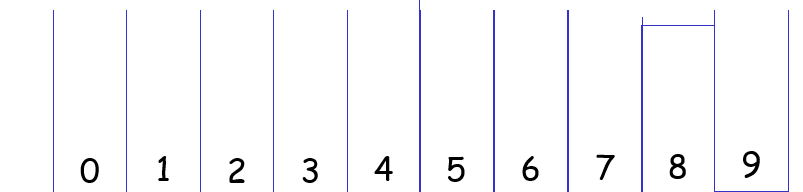
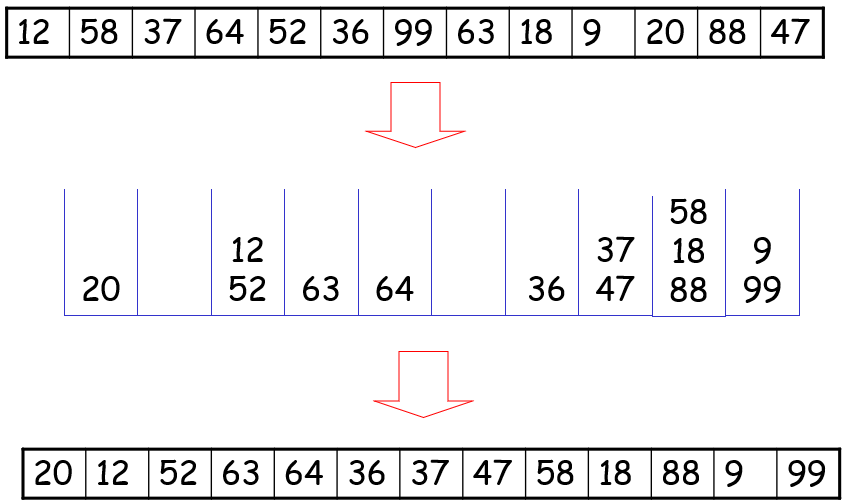
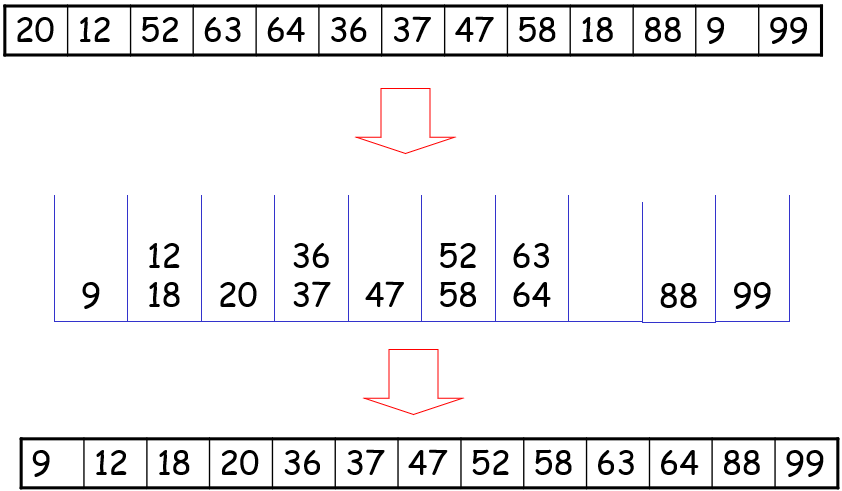
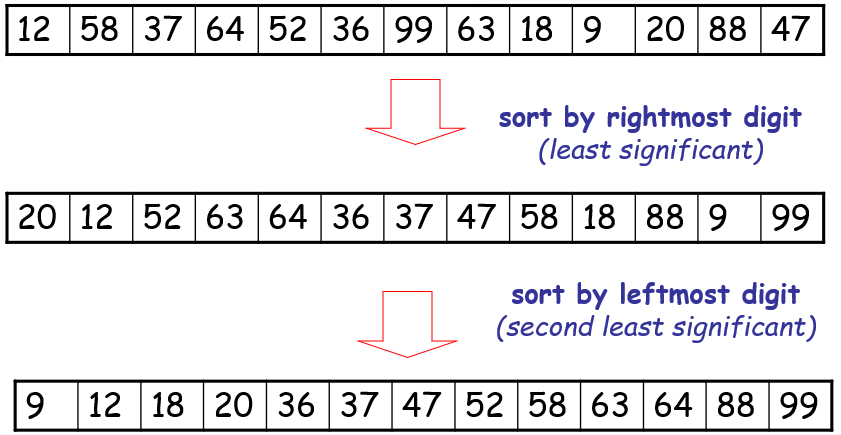
Question : Apply Radix sort Algorithm to sort the given sequence
12, 58, 37, 64, 52, 36, 99, 63, 18, 9, 20, 88, 47
Solution: (click for video explantion)
Since all data elements are integers, 10 buckets are required numbered 0-9 as follows, buckets are empty initially.
The entire process requires two passes as maximum number in the sequence consist of 2 digits.
Therefore, the sorted sequence is achieved by undergoing passes as follows
Problems on Red Black (RB) tree
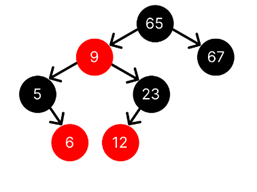
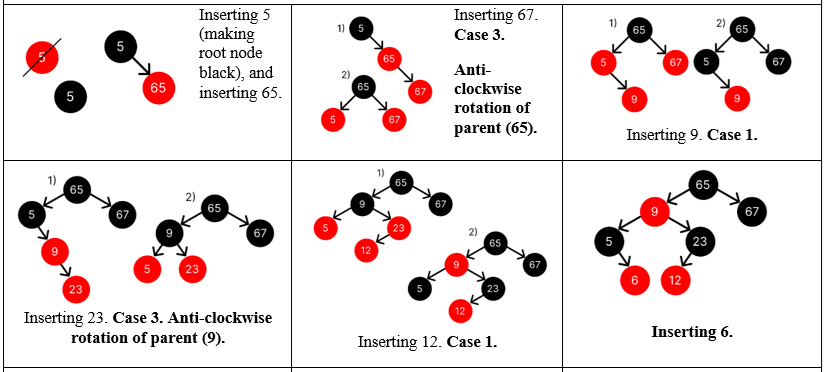
Question : Construct the RB tree by inserting following nodes
5, 65, 67, 9, 23, 12, 6
Solution ( click for video explanation )
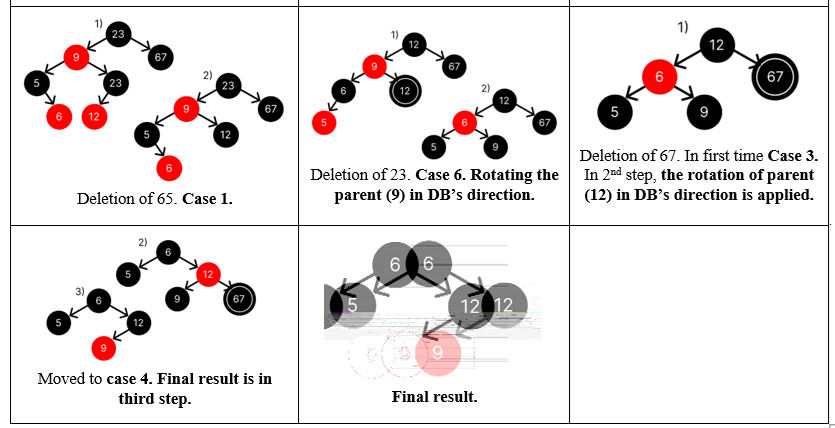
Question : Delete from the RB tree following nodes 65, 23, 67
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
Operations on Order Statistic Tree & Intreval Trees
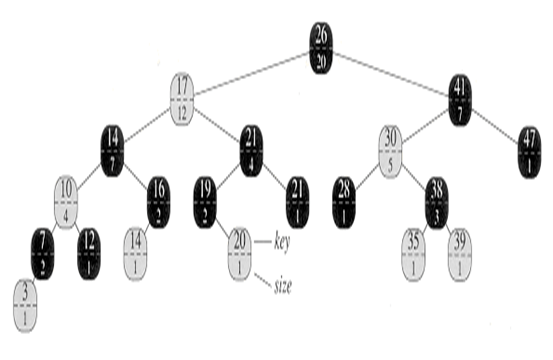
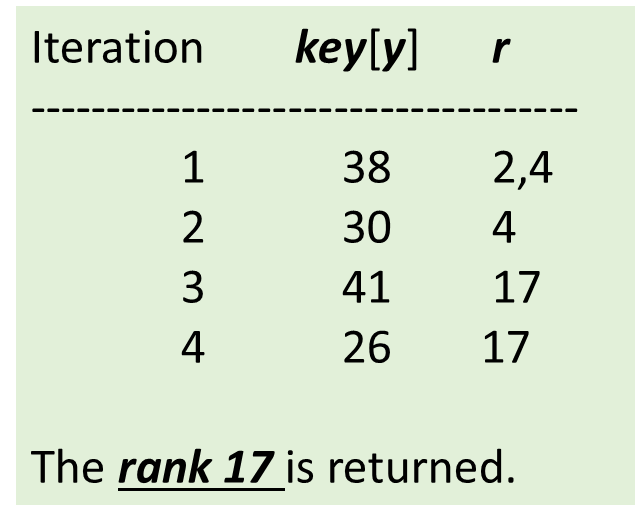
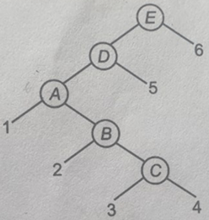
Question : Find the Rank of key 41 and key 38 in the following order-statistics tree
Note : ( click for video explanation )
Rank of Key 38 –Solution as follows
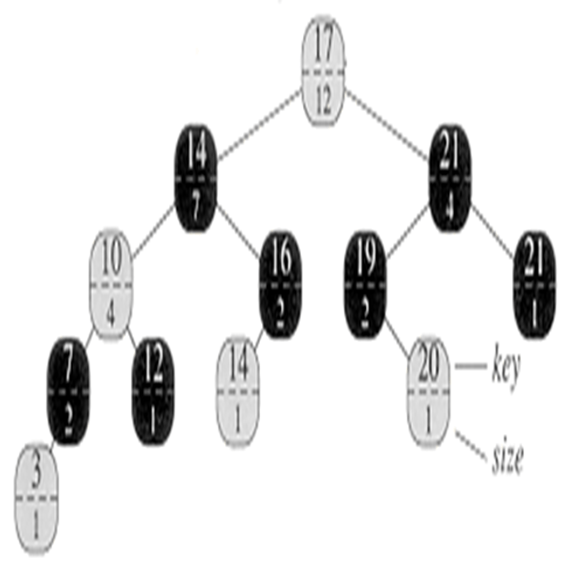
Question : Find the 7th smallest in the following order-statistics tree
Solution – 7th smallest is found as follows
| key | i | r |
| 17 | 7 | 8 ( i < r ) |
| 14 | 7 | 5 ( i > r ) |
| 16 | 2 | 2 ( i = r ) |
7th smallest is Key 16
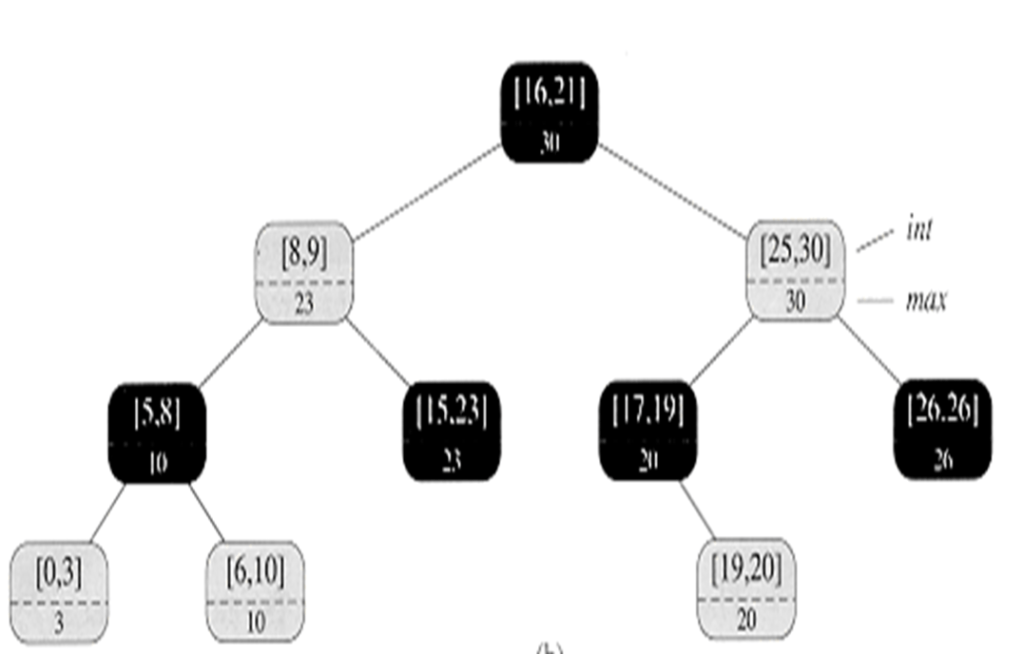
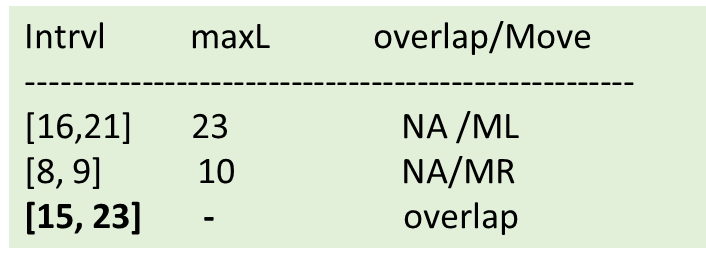
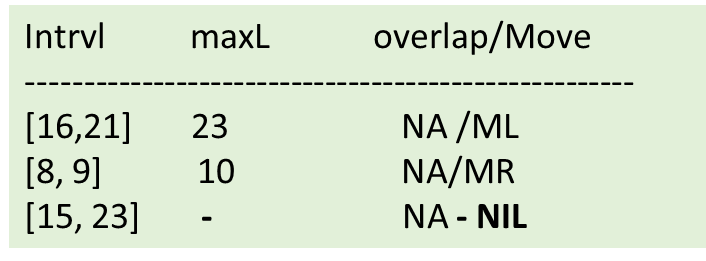
Question : Find the Interval [22, 24] in the following Interval tree
Question : Find the Interval [11, 44] in the above Interval tree
Explanation (click for video explanation)

Splay Tree Operations
Question : Splay node C in the following tree
Solution : ( click for video explanation )
Question : Splay node A in the following tree
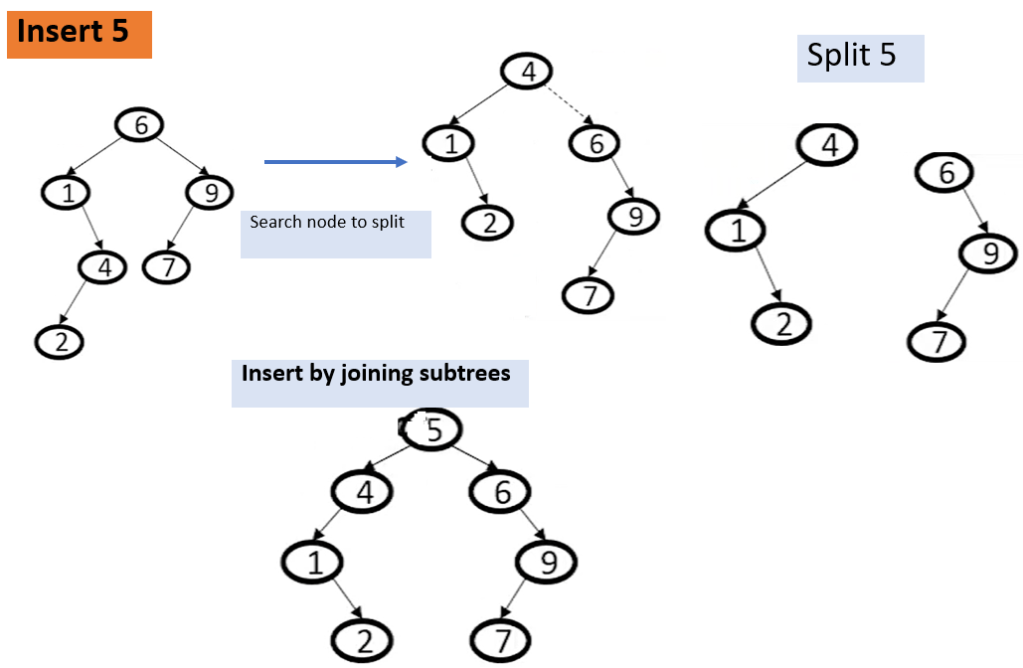
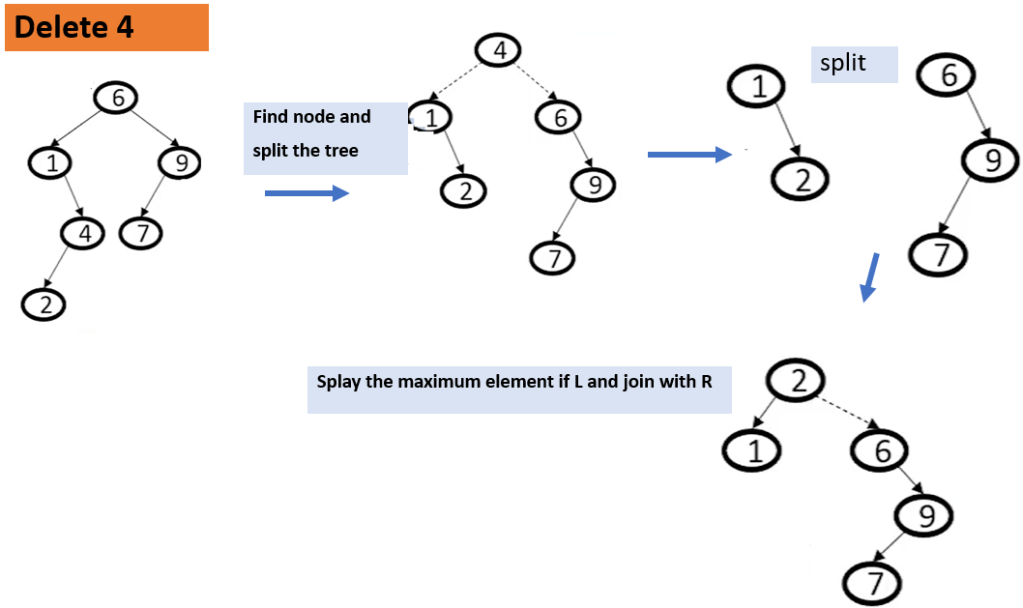
Question : Insert Node with Key value 5 in Splay tree using Split Method (click for video explanation)
Question : Delete Node with Key value 4 in Splay tree using Split Method click for video explanation)
Problems of Minimum Spanning Tree ( MST )
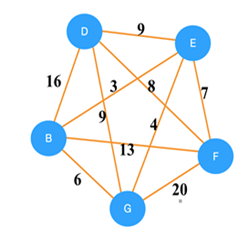
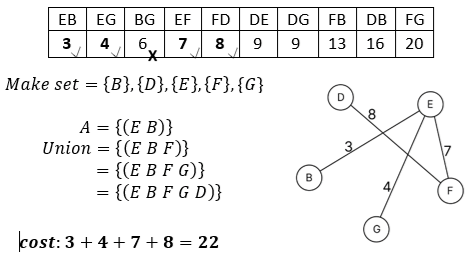
Question : Finding the MST using Krushkal method, also find the cost of MST.
Solution : Detailed steps as follows ( click for video explanation )
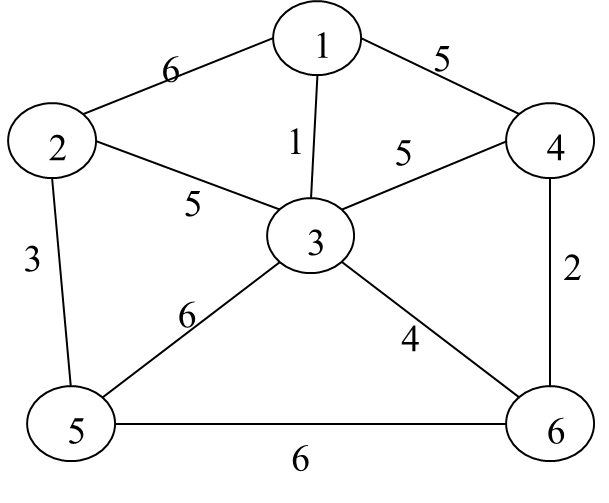
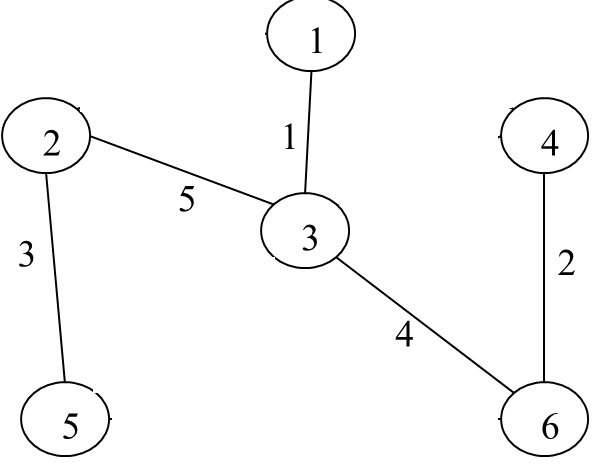
Question : Finding the MST using PRIMs method, also find the cost of MST
Solution : Detailed steps as follows (click for video explanation)
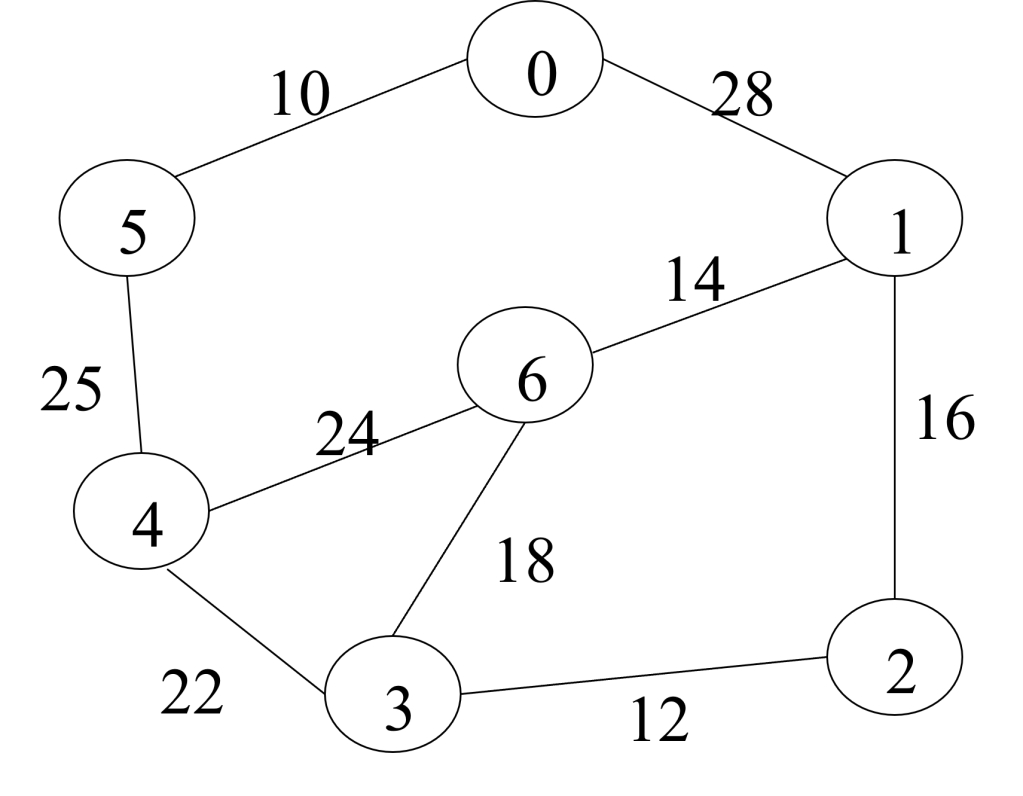
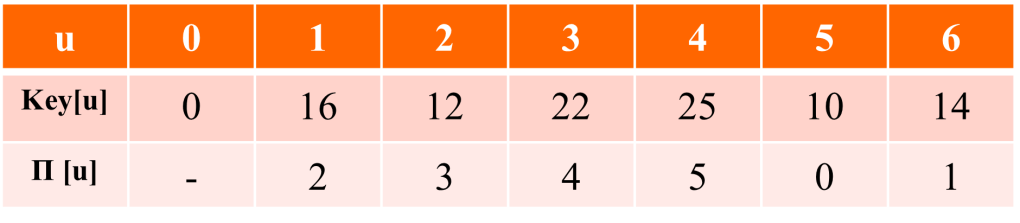
Question : Following information is derived using PRIMs algorithms for the graph , Find the MST
Solution : MST shown as follows (click for video explanation)
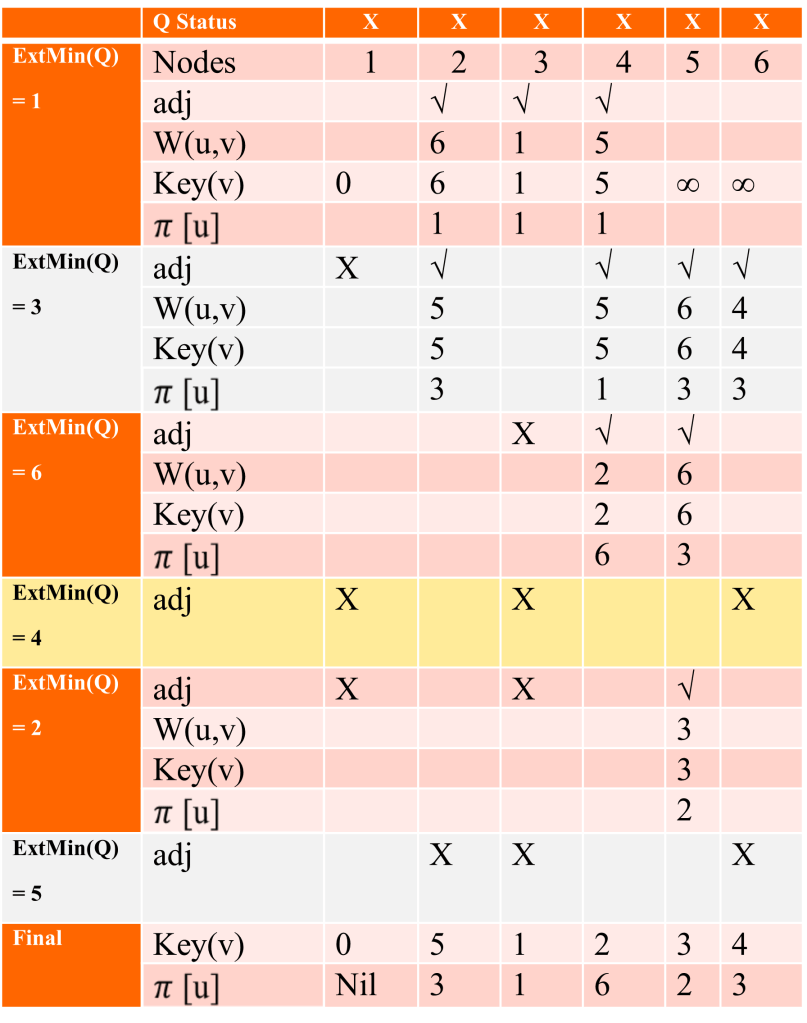
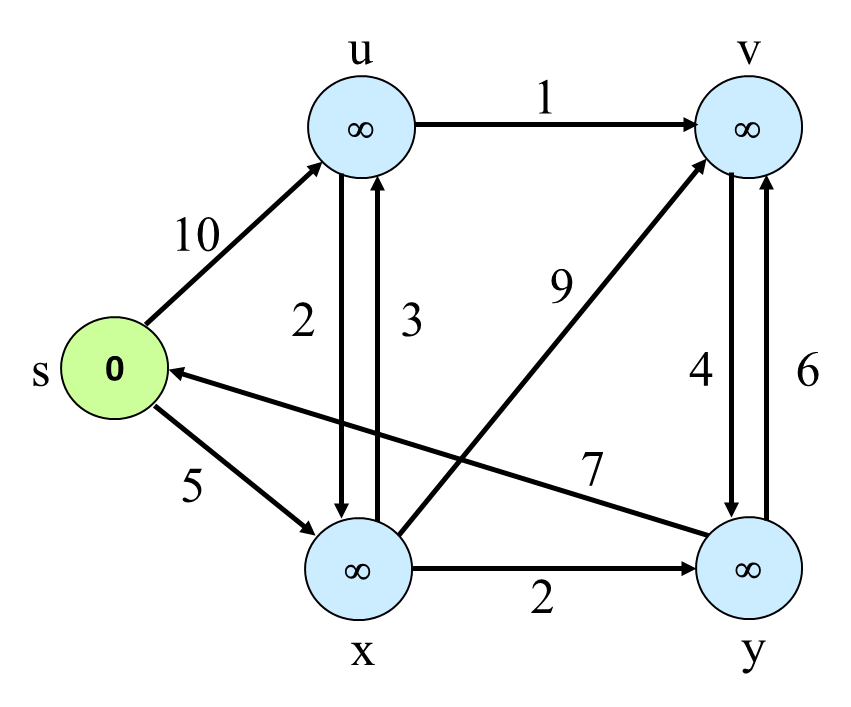
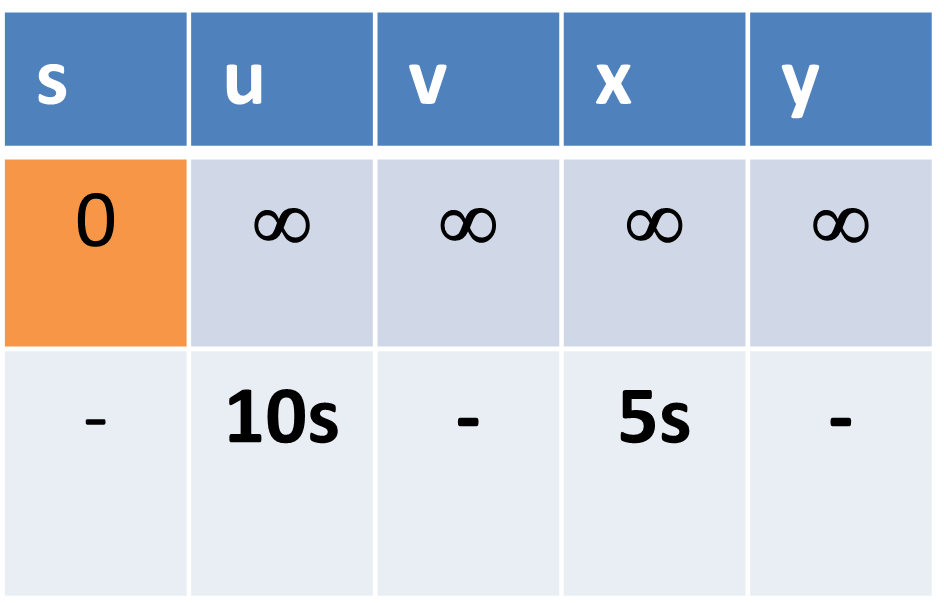
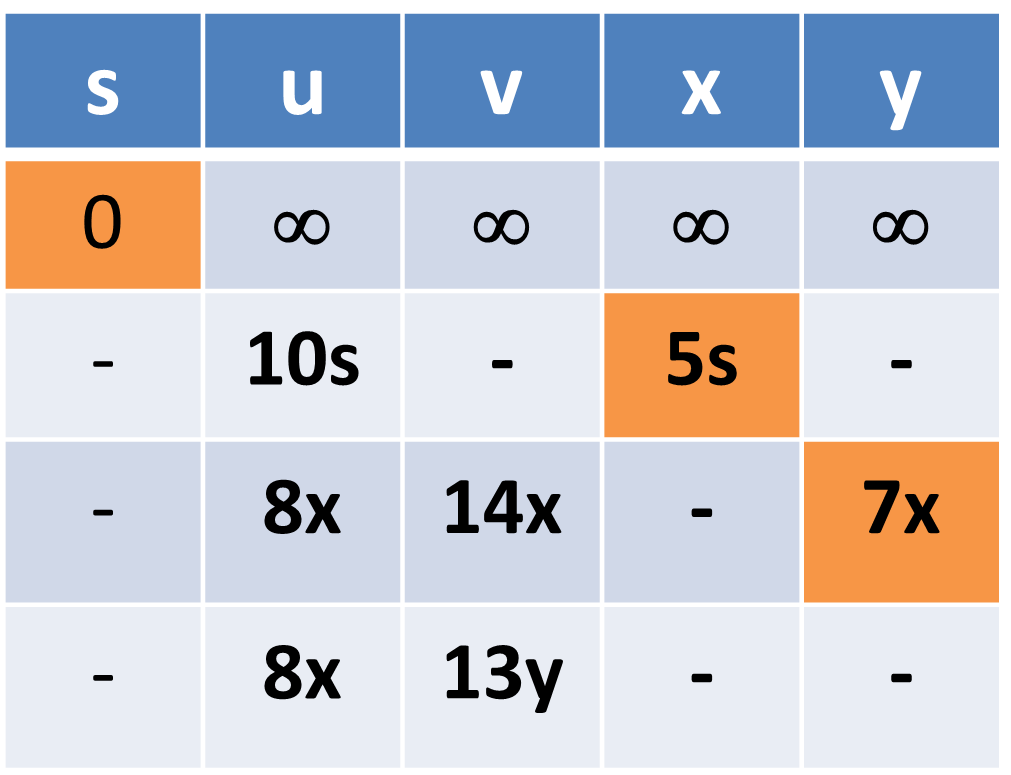
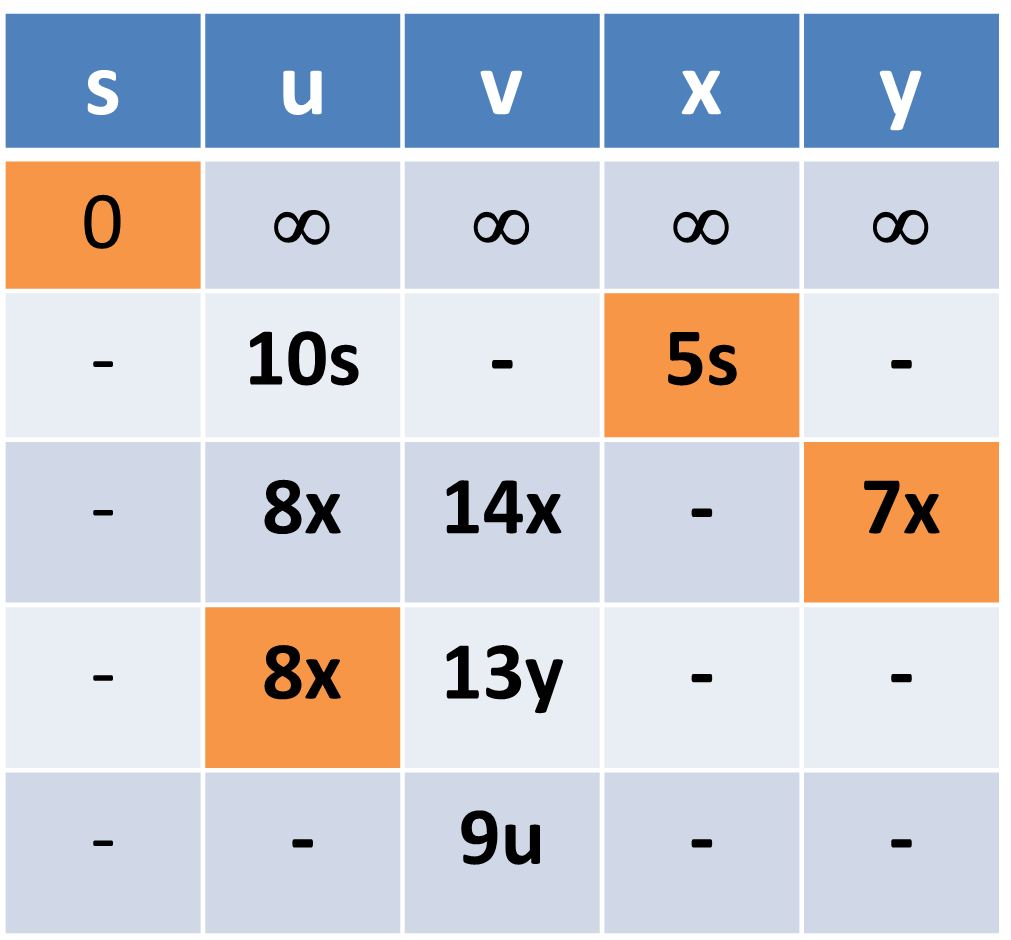
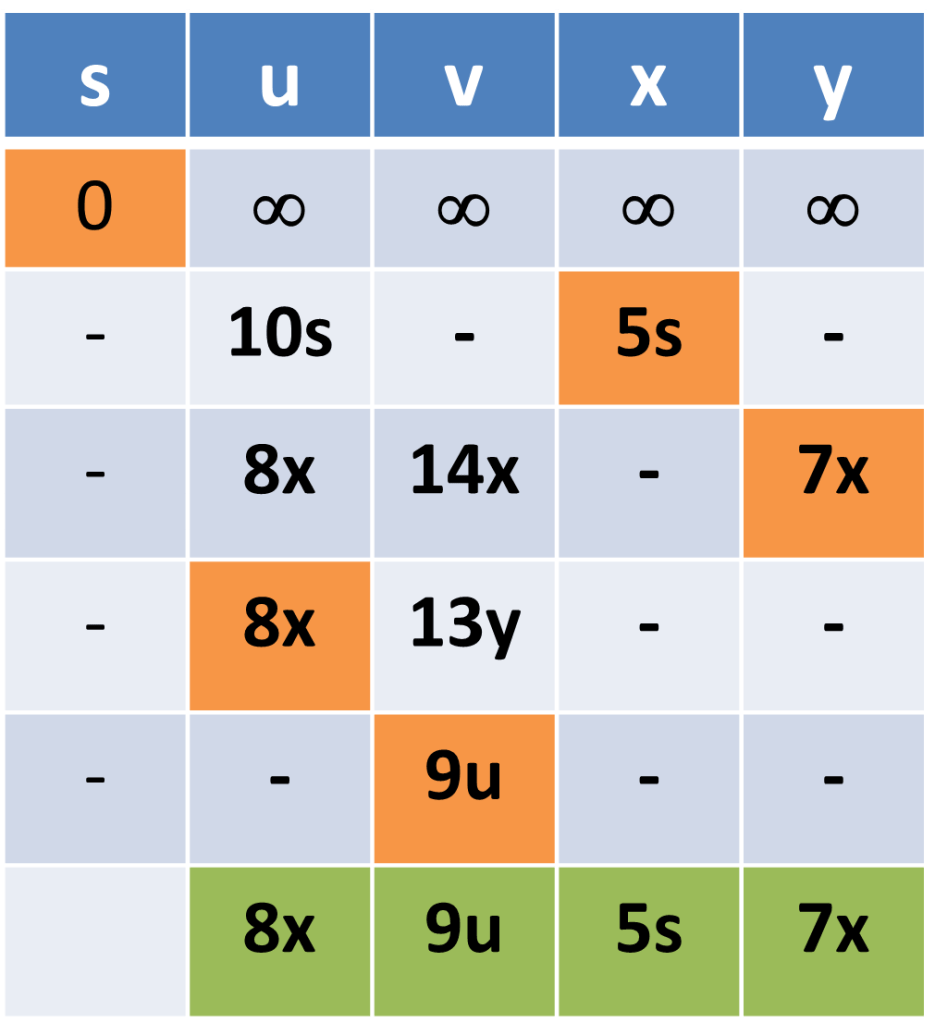
Question : Find shortest path from vertex S to all other nodes using Djikshtra Algorithms
Solution : Detailed iterations are shown as follows ( click for video explanation )
Final Answer
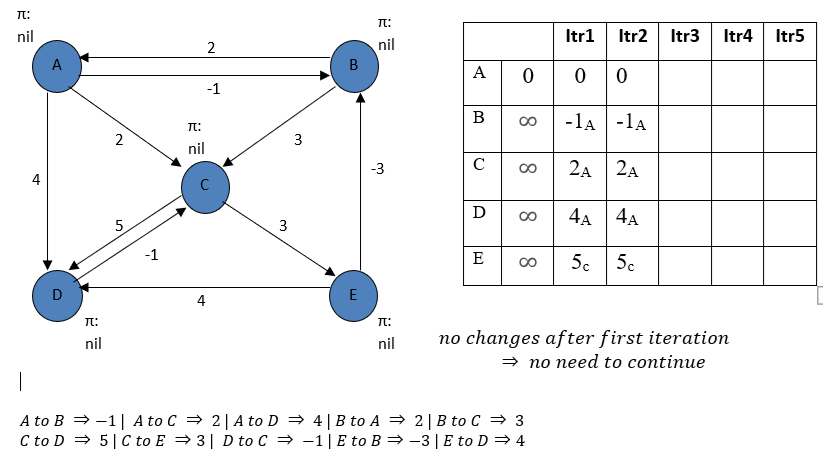
Question : Find shortest path from vertex A to all other nodes using Bellman Ford Algorithm
Solution : Detailed iterations are shown alogside ( click for video explanation )
Solving 0/1 Knapsack and Fractional Knapsack using Greedy Approach
Solve the following knapsack problem for following data values and knapsack capcity =60 kg
| Item | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 |
| Weight(kg) | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Value | 30 | 20 | 100 | 90 | 160 |
Solution – First find the preciousness of each item to make decision (click for video explanation)
| Item | val | Wt | Val/wt | Rank | Item Selected |
| I1 | 30 | 5 | 30/5 = 6 | 1 | Yes |
| I2 | 20 | 10 | 20/10 =2 | 5 | No |
| I3 | 100 | 20 | 100/20 = 5 | 2 | Yes |
| I4 | 90 | 30 | 90/30 = 3 | 4 | Yes |
| I5 | 160 | 40 | 160/40 = 4 | 3 | No |
Solving 0/1 Knapsack – Item selected based on rank (Greedy approach -select most precious item)
First Choice -Item 1 (5 kg) = > yes (capacity remaining = 60 – 5 = 55)
Second Choice -Item 3 (20 kg) = > yes (capacity remaining = 55 – 20 = 35)
Third Choice -Item 5 (40 kg) = > No (capacity remaining = 35)
Fourth Choice -Item 4 (30 kg) = > yes (capacity remaining = 35 – 30 = 5)
Fifth Choice -Item 2 (10 kg) = > No (capacity remaining = 5)
Total Gain attained by Items (val of I1+I3+I4) = 30+100+90 = 220
Note – this is NO optimal solution (optimal will be attained by selecting Item3 and Item5 (i.e. 100+160= 260), therefore, thus 0/1 Knapsack cannot be solved optimally using Greedy Method
Solving Fractional Knapsack – Item selected based on rank (select most precious item)
First Choice -Item 1 (5 kg) = > yes (capacity remaining = 60 – 5 = 55)
Second Choice -Item 3 (20 kg) = > yes (capacity remaining = 55 – 20 = 35)
Third Choice -Item 5 (40 kg) = > Yes (capacity remaining = 35, so take fraction of item i.e. 35 kg)
For Item5=> 40 kg has value 160, therefore 35 kg has value 140
Total Gain attained by Items (val of I1+I3+I5) = 30+100+140 = 270
Note – this is Optimal solution, thus Fractional Knapsack can be solved optimally using Greedy Method (optimal will be attained by selecting Item3 and Item5 (i.e. 100+160= 260)
Knapsack Problem using Dynamic Programming
Question : Solve the Knapsack Problem using Dynamic programming for following 3 items
Weight <2, 3, 4, 5> Value <3, 7, 2, 9> knapsack Capacity = 5 kg
Solution : The detailed solution is shown in table below ( click for video explanation )
| Cost | Weight | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| I0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 3 | 2 | I1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 7 | 3 | I2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 10 |
| 2 | 4 | I3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 10 |
| 9 | 5 | I4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 10 |
Answer => Items identified = Item1 and Item 2, Maximum Gain = 10
String Matching problems
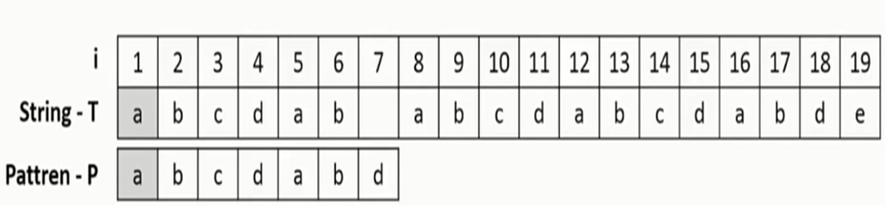
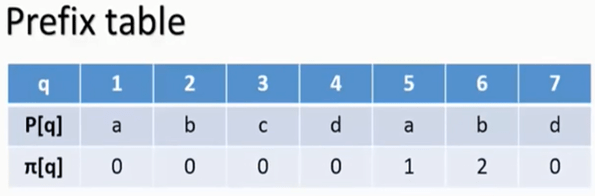
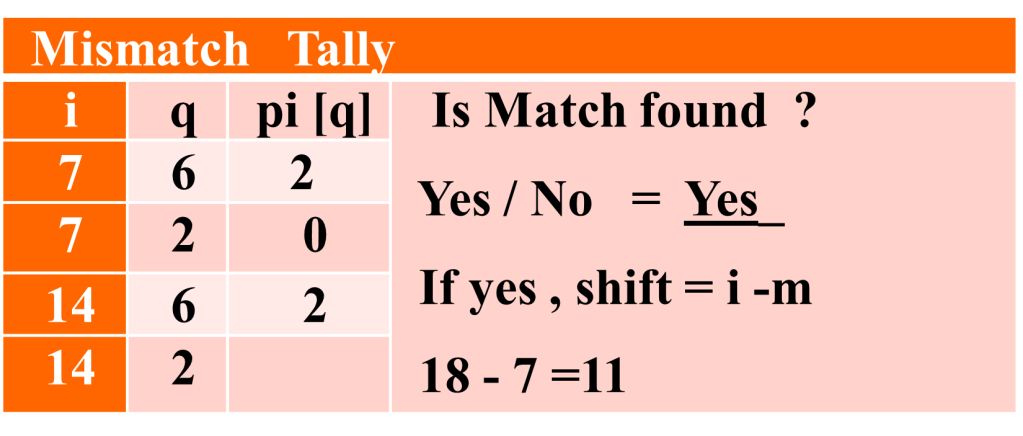
Ques : FInd the Pattern in the given Text using KMP algorithm
Solution – First find the Prefix table as follows (click for video explanation)
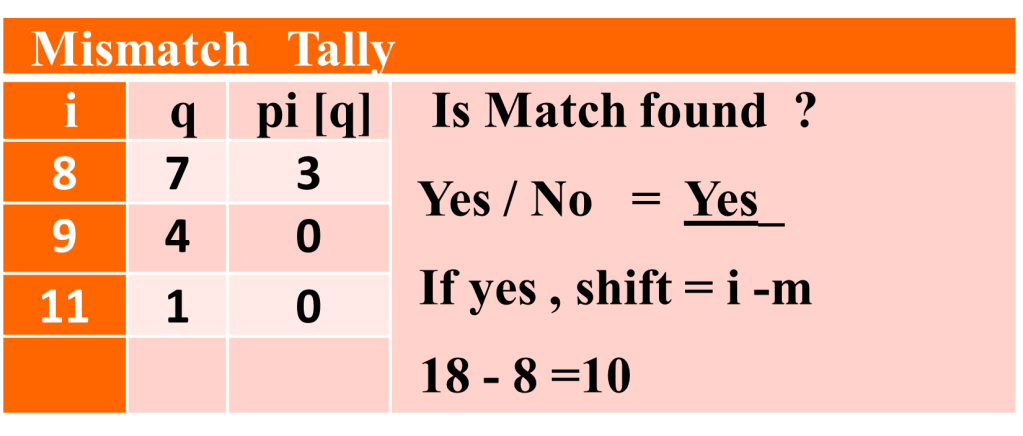
The shift made during the process is shown alongside. i is used to an index of Text, q is number of characters in Pattern found matched with Text, pi[q] refers to value in prefix table and will be used whenever mismatched is found. The Pattern is found in Text at 11th shift
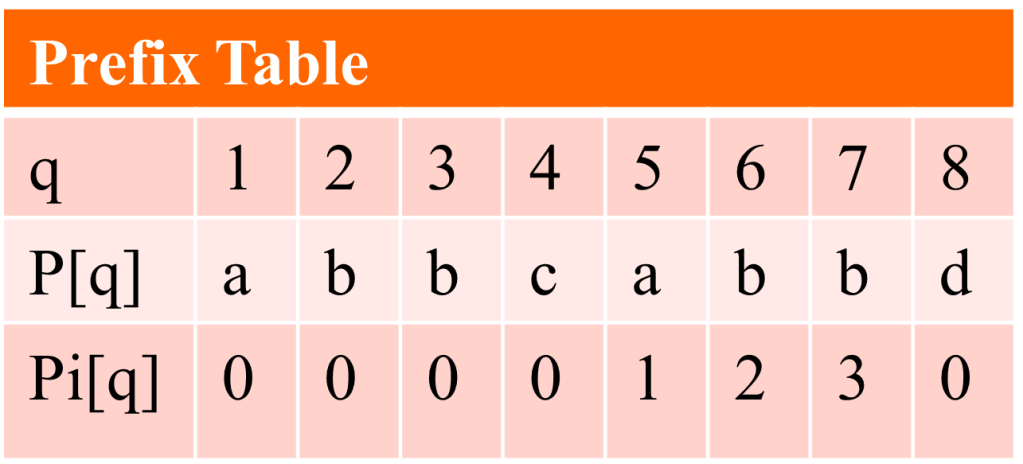
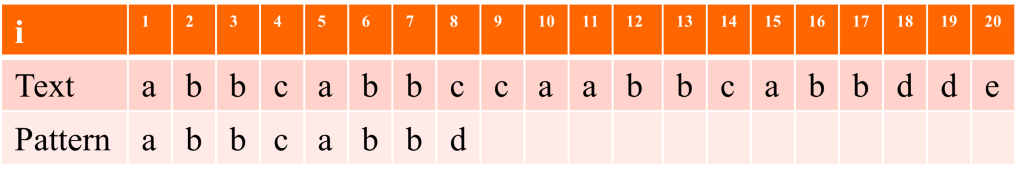
Ques : FInd the Pattern in the given Text using KMP algorithm
Text : abbcabbccaabbcabbdde Pattern : abbcabbd
Solution – First find the Prefix table as follows
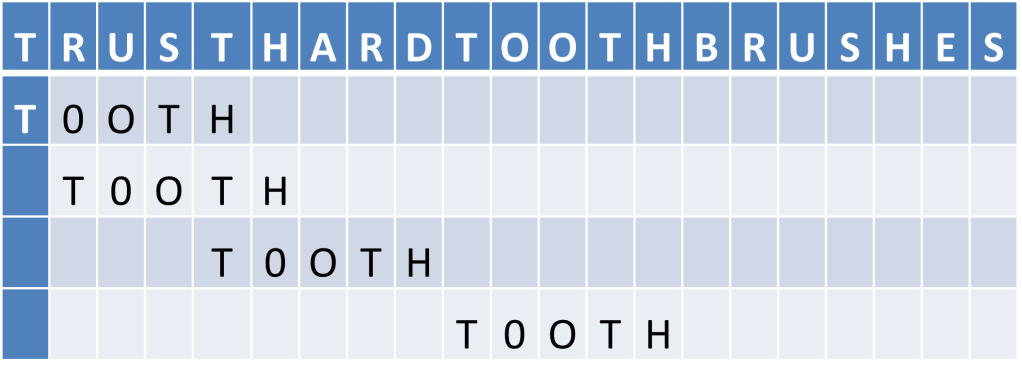
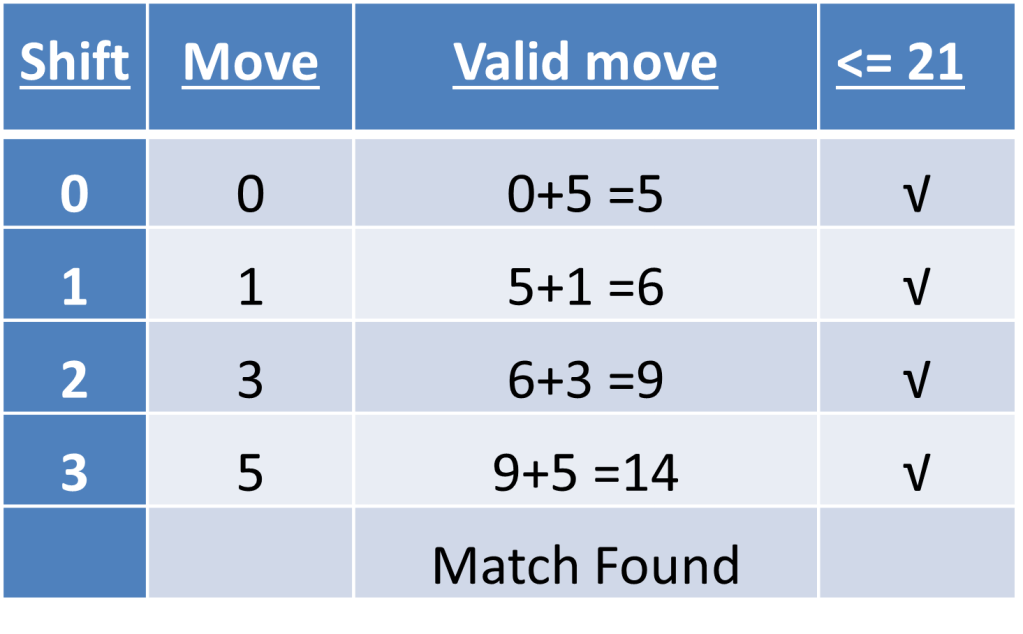
Ques : FInd the Pattern in the given Text using Boyers Moore algorithm
Text : trusthardtoothbrushes Pattern : toothd
Solution – First find the Bad Match table as follows (click for video explanation)

Constructing Bad-Match table
Value = length – index -1 ( index starts with 0)
Last letter = length , if not already defined
Every remaining letter (*) = length - i
Note:Shifting for cases would be used as (value – i), where i is the number of matched characters
Shift are shown as below