Linked List is a commonly used linear data structure which consists of group of nodes in a sequence. Each node consists of two fields which holds data and the address of the next node. This connection of nodes in a sequence makes a linked list. It is primarily used in trees and graphs based representations. A linked list is a dynamic data structure which means that the number of nodes in a list is not fixed and can grow and shrink on demand. Any application which has to deal with an unknown number of objects will need to use a linked list.
Representation of Linked List
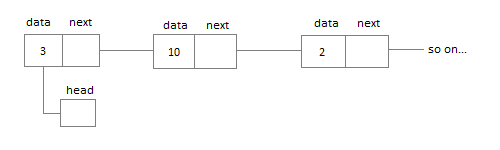
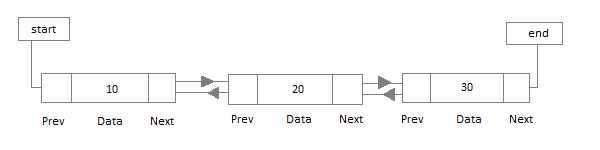
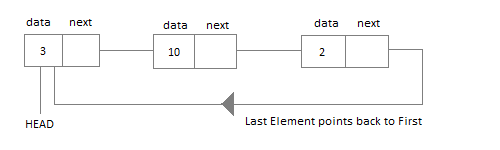
Applications of Linked List
- To implement many data structure for dynamic allocation like Stacks, Queues etc.
- To implement the Adjacency list representation of Graph.
- To implement Hash Tables – Ex. Open Chain Hashing (Each Bucket of the hash table can itself be a linked list.
- To represent a polynomial by simply storing the coefficient and exponent of each term.
- To implement “Undo” functionality in many software such as Photoshop or Word by storing Linked list of states.
- Operating System maintains and control all the running applications by creating circular linked list
Lets develop good understanding of Linked List and its various operation. [Click the following links to watch the video]
- Basics of Linked List
- Inserting Node to Single Linked List [read text] [download text]
- Deleting Node from Single Linked List [read text]
- How to Insert Node in Circular Linked List [read text]
- How to Delete Node from a Circular Linked list [read text]
- How to Add Node to Doubly Linked List
- How to Delete Node From a Double Linked List
- Analysis of Linked List Operations
You are invited to raise queries by writing your question in the box given below
Good day everyone!
Here is my question. Why should we use linked list, when we can use simple arrays which can access elements much faster? Thank you ahead!
The primary reason to use linked list is dynamic memory allocation which means you can allocate memory at run time whenever it is actually needed, thus no memory reservation is required.
Secondly linked list also support optimal memory utilization.
But if you want delete one element in linked list it will be much easier than array
Here is what i found about to share !
pros :
can be increase/decrease the number of nodes (dynamic allocation)
can use multiple data types as elements
so basically its advanced than arrays.
cons :
consumes more memory than arrays
need to clear memory once we done with it.
handling pointers is a bit tricky compared to arrays.. (but its needed for real time usage)
Good day everyone.
Dear professor why in your lectrue video you wrote that deletion of the last and first node of the circular list is O(n). I think that deletion of last and first node of circular list is O(1) since class “CircularLinkedList” have reference to last node so its deleteion will be O(1) we do not need to search last node in order to delete it. And similarly if we are going to delete first node we can find it by reading “Next pointer” of last node. Am I wright or not?
You are correct, in general, there are two different ways to implement it.
1. Assume “Last” points to first node of Linked list, following logic will be used
new_node->next= last;
last=new_node;
then we need to get the last node address also
last_address=getLastAddress(); (by using some function call) [this part is required to maintain circularity]
last_address=new_node;
Running Time = 0(n)
2. Assume “Last” point to Last node
new_node->next= last->next;
last->next=new_node;
Running Time = 0(1)
Thank you for reply professor. And what case should we take by default?
In general, the default time would be 0(1) but If it is mentioned that implementation hold only first address of node, then running time will be 0(n).
Good evening I have one question about linked list that does Head have its own data value or is it possible?
Thank you for answers
HEAD – Node is only meant to connect the first node …it does not hold any data except the address of very first node